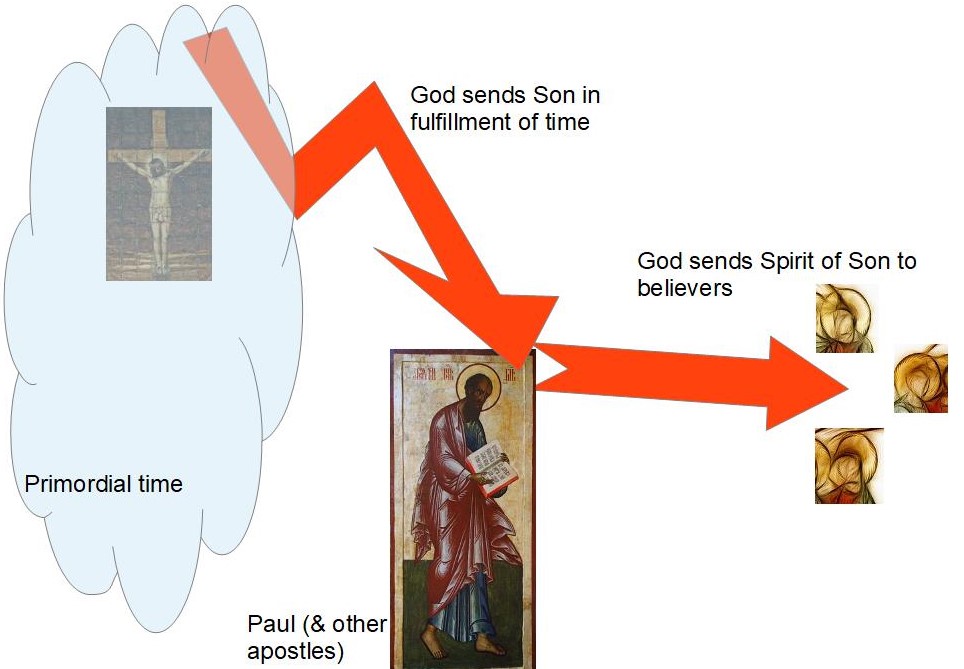
Those quotes are from Benjamin Reynolds, page 29 of his essay “The Gospel of John’s Christology as Evidence for Early Jewish Messianic Expectations: Challenges and Possibilities” for Reading the Gospel of Johns Christology as Jewish Messianism (2018). The hypothesis being advanced is that the Christology in the earliest Christian texts — a preexistent, heavenly messiah, sitting alongside God, was also the human messiah who died — can be explained with reference to messianic ideas in Second Temple Judaism.
Since I have been posting on Daniel Boyarin’s articles recently it is time to offer some “balance” and quote from William Horbury’s Jewish Messianism and the Cult of Christ (1998).

What can be the relevance of post Second Temple era rabbinic texts?
The Targums and rabbinic literature are considered from time to time among the evidence which may shed light on Judaism at the time of Christian origins. Most of their wealth of material is later, but when viewed in conjunction with the Septuagint and the writings of the Second-Temple period they can be seen to preserve much exegesis and tradition which will have been current then. (3)
–o–
What are the respective roles of Judaism and gentile beliefs in the development of the Christ cult?
Early Christianity also offers signs of continuity with the developed messianic expectation of ancient Judaism, especially in respect of conceptual links between spirit and messiah, and those narratives of advent and reign which make up a kind of messianic myth. These developments of an inherited messianism were encouraged by its parallel continuation in the Jewish community throughout the period of Christian origins, and by the importance of ruler-cult under both Greek and Roman rule. Within Christianity the Christ-cult developed side by side with the cults of the angels and the saints. For all three customs there were Greek and Roman counterparts, but the origins lay in Jewish practice which had already been influenced by the Greek and Roman world. In the case of the Christ-cult, messianism in particular formed the link between Judaism and the apparently gentilic acclamation of Kyrios Iesous Christos. (4)
–o–
What are messianic prophecies about?
[M]essianic prophecies are not simply predictions of deliverance, but affirmations of the ideal of the Israelite state as it should be. (14)
–o–
What Old Testament figures appear to have influenced the development of messianic ideas?
Moses
(a) Moses is represented as a king in Ezekiel the Tragedian (probably second century BC), Philo, and much rabbinic tradition. . . . . A royal interpretation of Moses seems to appear in any case in Isa. 63. 11 , where Moses is the shepherd of the flock, and Exod. 4. 20 LXX , where he receives his sceptre from God. . . . . At the heart of the Pentateuch, then, is a figure which could be and was interpreted as that of a royal deliverer. Note that his pleading for his people (e.g. Exod. 32. 11, 32) and his rebuttal by them introduce an element of suffering into this royal picture. (31)
David
(b) David emerges as a suffering and humiliated yet ultimately victorious king, notably in Ps. 18 = II Sam. 22; Pss. 21-22 , and the psalms associated in their titles with his flights from Saul and from Absalom into the wilderness (3; 54; 57; 59; 62; 142); . . . . he is an exorcist (I Sam. 16. 14-23) and an inspired prophet (II Sam. 23. 1-7 ; cf. I Chron. 28.12, 19). . . . .
The suffering aspect of the royal figure of David goes unmentioned for the most part in sources from the time of Christian origins, but its biblical prominence in the histories and psalms will have kept it in view, as is suggested by the reference to David’s flight in Mark 2.25-26 and parallels. This aspect of the figure of David will then have contributed, together with the suffering of Moses noted above, to the messianic interpretation of the suffering servant of Isaiah and the smitten shepherd of Zechariah. (32-33)
The Servant of Isaiah 53
(c) The servant of Isa. 53 is interpreted as messiah in the Targum, but as victorious rather than suffering. This interpretation is not unnatural, for the passage is preceded by a prophecy of [redemption and followed by a vision of restoration]. . . . The Israelite king appears as a suffering servant in Ps. 89. 39, and the messiah is God’s servant in Zech. 3. 8. . . . . It was perhaps originally formed on the model of the suffering king, and a messianic interpretation was probably current in the Second-Temple period, but the passage was not then regarded as obviously messianic. (33)
Smitten shepherd of Zechariah 13:7
(d) The smitten shepherd of Zech. 13. 7 forms part of a series of prophecies in Zechariah, beginning with the advent of the lowly king in 9. 9, which find a messianic interpretation both in the New Testament and in rabbinic literature. In the latter they are associated with Messiah ben Joseph or ben Ephraim, who fights Gog and Magog and dies in battle. The death of a messiah is already envisaged in II Esdras 7, at the end of the messianic age, and the cutting off of a rightful ruler called messiah is foretold in Dan. 9. 26, quoted already. The notion of a slain messiah is then likely to have been current in the Second-Temple period, partly on the basis of Zechariah, although it seems clearly to have been less prominent than the expectation of a great and glorious king. The objections of the disciples to Christ’s expectation of suffering, as depicted in the Gospels, might then be ascribed not to their total ignorance of the notion of a humiliated messiah, but to their unwillingness to accept that it might apply in this case. (33)
The Son of Man in Daniel 7
(e) The Son of man in Dan. 7 is viewed messianically in the earliest interpretation, ranging from the middle of the first century BC to the middle of the second century AD in the Parables of Enoch, II Esdras, the Fifth Sibylline Book, a saying attributed to R. Akiba, and Justin Martyr’s Dialogue. In its setting in Daniel, however, it is widely taken at present to represent an angelic deliverer, probably Michael, the patron of Israel, who is mentioned as such in 12. 1. . . . This is an attractive view, because human figures often represent angels, in Daniel and elsewhere, and the importance of angels as
regulating terrestrial affairs is clear not only in Daniel but also in the Qumran War Scroll. Nevertheless, the early messianic interpretation seems more likely to be right. Both angelic and human leaders functioned in the Exodus, both are mentioned in the War Scroll, and both can be envisaged without difficulty in Daniel. In Daniel 2, the coming of the kingdom of God, represented by the stone which breaks the image, can naturally be associated with a messianic figure, just as in the War Scroll the kingdom is said to belong to God pre-eminently at the moments when Israel is delivered by David, the kings of his line, or the messiah. In Dan. 7 the beasts represent kings or kingdoms (7. 17, 23-24), not the angel-princes who are the expected foes of Israel’s angel-patron (10. 13 , 20-21). Finally, the designation ‘Son of man’ is close to the use of various words signifying ‘man’ in pre-Danielic messianic oracles, including Num. 24. 17; II Sam. 23. 1 and Zech. 6. 12 , quoted above, and Ps. 80. 18, which has ben adam. (34)
Conclusion
Of these five figures, then, Moses, David, the smitten shepherd and the Son of man will have influenced the growth of messianism from the first. In each case they fitted well into the royal messianism which we have seen to predominate, despite the importance of dual messianism. In the end the servant of Isa. 53 also contributed to the picture of the messianic king. (34)
Continue reading “Horbury Argued Similarly: Jewish Messianic Ideas Explain Christianity”