This post is a continuation of Invitations to Watch a Martrydom: The Letters of Ignatius (or Peregrinus). . .
|
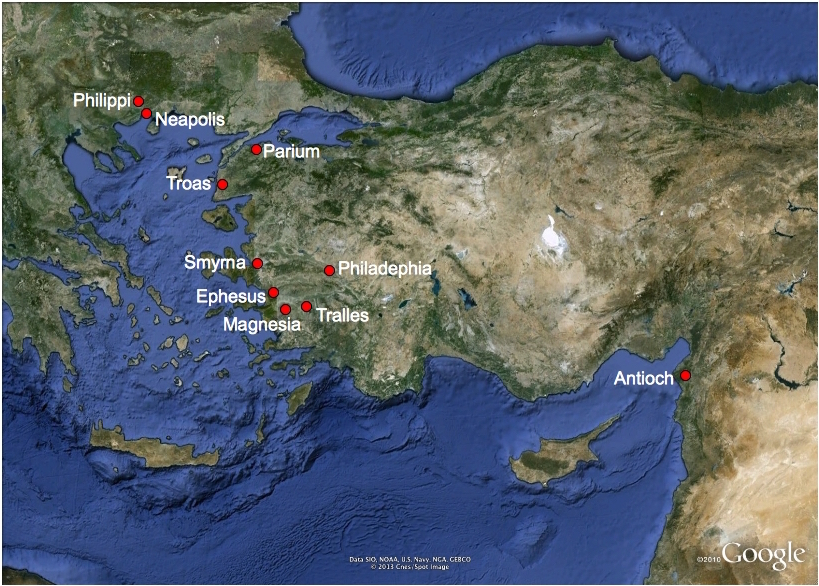
In my previous post I argued that the so-called letter to Polycarp was originally a letter from Peregrinus to the man who, after restoring order in the church of Antioch, had been installed as that church’s new bishop. The letter was one of three that the prisoner wrote after learning that the dissension in the church in Antioch had come to an end. In the other two letters (those addressed to Smyrna and Philadelphia) he urgently requested that Ambassadors of God be appointed to go to Antioch to rejoice with that church. In the so-called letter to Polycarp, on the other hand, there is an urgent request for the convocation of a most God-pleasing council and, in connection with it, the appointment of a Courier of God. This most God-pleasing council, I maintain, was convened in Antioch— not Smyrna—and it is one and the same with the gathering mentioned in Lucian’s TDOP* that drew delegates “even from cities in Asia to succour, defend and encourage” the would-be martyr Peregrinus.
|
CONTENTS OF THIS POST:
(added by Neil)
Two sets of letters
The letter to the Romans
Originally written to the church at Antioch
The route
Problems with traditional reconstructions
The Peregrinus hypothesis removes these problems
A plausible reconstruction
The Peregrinus hypothesis removes difficulties found in the letters
A telltale expression
A phrase seen as relatively insignificant by commentators is shown to occur consistently in a certain context and accordingly adds weight to the hypothesis that the letters were originally written by Peregrinus on his way to Antioch.
.
Two sets of letters
The letters to Philadelphia, Smyrna and to Polycarp purport to have been written from the port city of Troas while the prisoner was waiting to board ship. But, as we will see shortly, they were probably written while he was waiting at a different port.
The other letters in the collection—to Ephesus, Magnesia, Tralles and Rome—were written before the prisoner knew the outcome of the in-fighting at Antioch. Because the four letters in this group would have been written at least a few days before the three letters in the other group I will refer to them, for the sake of brevity, as set 1 and will call the others set 2.
The set 1 letters were written in Smyrna during a stop there by the prisoner’s military escorts. The bishops of three of the churches addressed by those letters—Ephesus, Magnesia and Tralles—had traveled, accompanied by a few other members of their flocks, to visit with the prisoner at Smyrna. The letters written to their churches were likely carried back by them when they made their return trips. I see no serious reason to question that these three letters were in fact addressed to the churches they purport to address. I cannot say the same about the other set l letter: Romans.
.
The Letter to the Romans
The message of the letter to the Romans is loud and clear. It is basically a sustained plea: “Don’t try to get me released, for I want to die for the Name.” Continue reading “Making Sense of the Letters and Travels of Ignatius (Peregrinus?)”