When starting this post I had hoped it would complete my discussion of Robert M. Price’s chapter, “Does the Christ Myth Theory Require an Early Date for the Pauline Epistles?” in ‘Is This Not the Carpenter?’. This was meant to address Price’s reasons for thinking that the gospel narratives of Jesus — or any stories of an earthly life of Jesus — first made their appearance well into the second century. I have sometimes argued the same, but Price does so from a quite different perspective (drawing on what we know of Marcion and early Marcionism) from anything I had considered.
When starting this post I had hoped it would complete my discussion of Robert M. Price’s chapter, “Does the Christ Myth Theory Require an Early Date for the Pauline Epistles?” in ‘Is This Not the Carpenter?’. This was meant to address Price’s reasons for thinking that the gospel narratives of Jesus — or any stories of an earthly life of Jesus — first made their appearance well into the second century. I have sometimes argued the same, but Price does so from a quite different perspective (drawing on what we know of Marcion and early Marcionism) from anything I had considered.
Before getting into Price’s argument some background was necessary. Unfortunately or otherwise, that background turned into a substantial post of its own, so here it is now. Price’s arguments for a second century creation of the gospels will have to wait. This post continues Price’s comparative study of early mythicist views of the relationship between Paul’s letters and the narratives of Jesus found in the gospels. Regardless of the date of Paul’s letters, this has long been the foundation of the Christ Myth theory.
As I pointed out in the first post on this chapter, Price discusses the views of today’s pre-eminent mythicists, G. A. Wells and Earl Doherty, noting their preference for the orthodox view of the Pauline epistles. That is, that they are written by “the genuine” Paul and thus belong to the middle of the first century, well before the gospels were penned.
It is now necessary to look at the earlier arguments for sake of comparison, as Price does.
.
Paul-Louis Couchoud

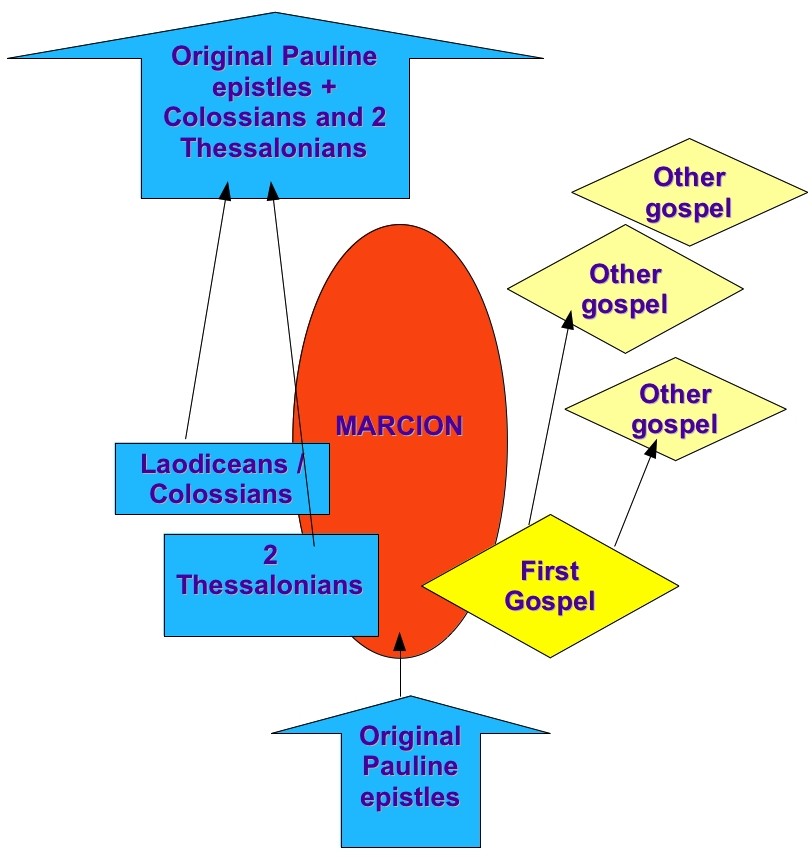
Paul-Louis Couchoud accepted the genuineness of Pauline letters “at least in their shorter, Marcionite editions”.
He argued that Marcion penned 2 Thessalonians and Ephesians (known originally as Laodiceans) , but also that he wrote the first gospel — after the Bar Kochba revolt (133 c.e.) — and lived to see other gospels expand upon his.
Price sees here a potential acceptance of the possibility that one could write “Pauline” letters that contained no hint of a historical Jesus even though one was aware of a narrative of such a Jesus. But Price also concedes that in this case there was little opportunity for biographical references to Jesus to appear in letters that were written in direct response to, or as commentaries upon, earlier letters (1 Thessalonians and Colossians.) Continue reading “Early Christ Myth Theorists on Paul’s and the Gospels’ Jesus: ‘Is This Not the Carpenter?’ ch. 6 continued.”