Here we look at the sources in the Jewish Scriptures for:
a. John the Baptist
b. the Baptism of Jesus
c. the wedding at Cana
d. the three temptations of Jesus in the wilderness
Musings on biblical studies, politics, religion, ethics, human nature, tidbits from science

Here we look at the sources in the Jewish Scriptures for:
a. John the Baptist
b. the Baptism of Jesus
c. the wedding at Cana
d. the three temptations of Jesus in the wilderness

Continuing from Ascension of Isaiah: Other Questions. . . .
. . . .
Earl Doherty without doubt was the major contributor to the Jesus myth perspective from the 1990s through to the early 2000s. I highly respected his grasp of both the big picture and the detail, his clear-headed engagement with the scholarship, and his alertness to valid logical reasoning. His discussion of the Ascension of Isaiah in The Jesus Puzzle and again and in greater depth in Jesus Neither God Nor Man have been mainstays in my own attempts to learn more about that ancient text. James Barlow has delved into the Asc. Isa. in even more detail since and finds even more support for Doherty’s view that it contains evidence of a heavenly crucifixion of Jesus and that its passage of an earthly sojourn of Jesus in one manuscript is a later addition.
In this post I would like to revisit some of Earl Doherty’s discussion about the Asc. Isa.. (I will return in later posts to addressing James Barlow’s thoughts.)
On page 106 of The Jesus Puzzle Doherty writes:
Here is the key passage. The seer and his angelic guide have reached the seventh heaven. There they see the Lord, the Christ, and the angel foretells this to Isaiah (9:13-17):
13 The Lord will descend into the world in the last days, he who is to be called Christ after he has descended and become like you in form, and they will think that he is flesh and a man.
14 And the god of that world will stretch out his hand against the Son, and they will lay their hands upon him and hang him upon a tree, not knowing who he is.
15 And thus his descent, as you will see, will be concealed from the heavens, so that it will not be known who he is.
16 And when he has plundered the angel of death, he will rise on the third day . . . .
(I have reformatted Doherty’s text and added underlining.)
The underlined section, more fully discussed in Jesus Neither God Nor Man, are quite possibly later additions. It does not appear in all manuscripts. At least one scholar of the Asc. Isa., Michael Knibb, proposes that all references to Jesus and Christ in the Asc. Isa. have been subsequently added. “They will think that he is flesh and a man” appears to be at odds with the rest of the Asc. Isa. that says Jesus will take on the appearance of lower angels, Doherty suggests.

In a shorter manuscript text we read “he will hang him upon a tree”,
showing that the focus is indeed on ‘the god of that world’ and not on any human agents on earth. The motif of not knowing who the Son is comes tellingly close to Paul’s “rulers of this age” (1 Cor. 2:8) who were ignorant of God’s purpose and inadvertently crucified the Lord of glory. Since the identity of the Son is declared to be concealed “from the heavens,” this ignorance is on the part of those in heaven, not on earth.
(JNGNM, 121f)
The shorter text (in Slavonic/Latin manuscripts) thus reads (using R.H. Charles’ translation):
13. The Beloved will descend . . . into the world in the last days . . .
14. And the god of that world will stretch forth his hand against the Son , and they will crucify him on a tree, and will slay him not knowing who He is. . . .
16. And when He hath plundered the angel of death, He will ascend on the third day . . .
(An aside at this moment: I wonder of Doherty’s view that “the world” to which the Beloved descends includes the firmament, and can mean events happening solely in the firmament, is worthy of more critical attention.)
Also of note, Doherty points out, is that the passage has no clear “Christian theology” of the cross. There is no “dying for sin” or idea of atonement. The death is “a simple rescue operation” to free the prisoners of Hades from the evil angels. Doherty goes even further:
If “Jesus” and “Christ” are later additions, we would not even be able to label this document ‘Christian’ but rather a case of Jewish sectarianism, although something that was in itself ‘proto-Christian.
(JNGNM, 123)
But we come now to that pocket gospel, the account in 11:2-22 of Jesus’ time on earth. In JNGNM Doherty heads his discussion
11:2-22 contains the account of the birth of Jesus, the actions of Mary and Joseph, Jesus performing miracles and his supporters being turned against him by demonic powers so that they hang him on a tree. Of this section Doherty states
There are many arguments to be made that the latter version should be considered a later expansion, despite Knibb’s opinion (p. 154) that “the primitive character of this narrative [11:2-22] makes it difficult to believe that it did not form part of the original text.”
(ibid)
Here are three arguments along with my thoughts on them. Continue reading “Ascension of Isaiah: Questioning Three of Earl Doherty’s Arguments”

Thomas Mann and Norman Ornstein show in It’s Even Worse Than It Looks that since the 1970s dominant forces within the Republican Party have been working to delegitimize their political opponents and erode public confidence in their political institutions. The authors focus in particular on Republican Party threats to bring down economic hardship on Americans if a Democrat President doesn’t yield to their demands — without any compromise. It’s a helpful little book that puts today’s surreal miasmic fog of words, claims, assertions, accusations into context.
 I was reminded once again of Charlie Kirk’s The MAGA Doctrine and how his political opponents are portrayed. They are not a Party to be reasoned with. The thought of compromise can never occur. The Party is a collection of people who are literal villains, evil characters who must be removed entirely from any position of influence.
I was reminded once again of Charlie Kirk’s The MAGA Doctrine and how his political opponents are portrayed. They are not a Party to be reasoned with. The thought of compromise can never occur. The Party is a collection of people who are literal villains, evil characters who must be removed entirely from any position of influence.
As an outsider, I look in vain for serious political debate between the two major parties in the US. What I see, instead, is one side constructing an Alternative Reality bubble. Their words only have meaning to anyone within that bubble and no-one else.
Obviously democracy can only work where there are tolerance and acceptance of the legitimacy of the other side’s position. Throw that out and we have a kind of intolerance that allows for no rational cooperation or reconciliation. That’s when one enters dangerous territory.
In this post I document one dataset of this delegitimizing process from The MAGA Doctrine by Charlie Kirk. This is a book that Donald Trump highly commends to his supporters. I take it as one fair indication of how the pro-Trump Republicans and associated far right supporters perceive their political opponents, the Democratic Party. Read the excerpts of what Kirk writes about his political opponents and see if you can find any room for serious discussion or debate. All quotes are from the electronic ePub edition, so no page numbers, sorry. By the way, as an Australian I find myself completely flummoxed by the very idea that any politician in the U.S. — Sanders or Ocasio-Cortez — is actually a “socialist”. Kirk’s understanding of “socialism” is simply perverse.
. . .
Democrats ignore facts; are deluded “socialists”.
All thanks to the free market socialists want to destroy. If anything, economic growth rates and progress have slowed in the past few decades as the welfare state, to which the socialists give all the credit for such advances, grew. The new socialists and Democrats steadfastly ignore these facts. And it is this delusion that makes the MAGA Doctrine more important than ever.
. . .
Democrats are immoral and tyrannical. Continue reading “The End of Political Debate and the Creation of Alternative Reality”

Continuing from Ascension of Isaiah: Questions. . . .
. . . .
Is the “pocket gospel” (an account Jesus’ earthly birth and crucifixion in 11:2-22 of the Ascension of Isaiah) an original part of the Ascension of Isaiah and not a later interpolation?
In the previous post we looked at one disputed reason to think so. Here we look at a couple more. (Like the first reason addressed these are taken from an early commentary on the Asc. Isa. by R.H. Charles.)
In the pocket gospel we read that no-one on earth recognizes who Jesus is, neither when he is a newborn arrival into the world nor when they crucify him. A long-standing argument that this mini-gospel of Jesus’ birth and death is original is that this theme of ignorance fits in nicely with the rest of the Asc. Isa..
Before we come to the pocket gospel in chapter 11 we read in chapter 9:
14. And the god of that world will stretch forth his hand against the Son, and they will crucify Him on a tree, and will slay Him not knowing who He is.
Even more often stressed in the lead up to chapter 11 is that no-one, no angel, no demon, will recognize Jesus as he passes through the lower heavens. Jesus will look no different from any of the other inhabitants of those spirit worlds. Thus in chapter 10:
9. And thou [God speaking to his Beloved, Jesus] wilt become like unto the likeness of all who are in the five heavens.
10. And thou wilt be careful to become like the form of the angels of the firmament [and the angels also who are in Sheol].
11. And none of the angels of that world shall know that Thou art with Me of the seven heavens and of their angels.
12. And they shall not know that Thou art with Me, till with a loud voice I have called (to) the heavens . . .
The disputed passage, the pocket gospel of 11:2-22, contains these matching statements:
12. And the story regarding the infant was noised abroad in Bethlehem.
13. Some said: “The Virgin Mary hath borne a child, before she was married two months.”
14. And many said: “She has not borne a child, nor has a midwife gone up (to her), nor have we heard the cries of (labour) pains.”
And they were all blinded respecting Him and they all knew regarding Him, though they knew not whence He was.
and
18. And when He had grown up he worked great signs and wonders in the land of Israel and of Jerusalem.
19. And after this the adversary envied Him and roused the children of Israel against Him, not knowing who He was, and they delivered Him to the king, and crucified Him, and He descended to the angel (of Sheol).
Now for the reason for thinking the latter passages are part of an interpolation:
If an editor wanted to continue to with the lack of recognition theme then it seems to be unlikely he would introduce details that seem to make that lack of recognition implausible. Why not simply continue the Asc. Isa. theme of having the Beloved look no different from those around him? That’s enough elsewhere. Why then have the Beloved appear in vision performing remarkable miracles that surely must give his identity away? One could go further and note that Jesus’ birth in Jerusalem was certainly not kept secret from anyone.
If the only purpose of the Beloved not being recognized was to have him killed so he could enter Sheol and recapture the dead back to life, thus defeating the power of the Angel of Death, then what point could there be to introducing other details of Jesus’ earthly sojourn that had to have been kept hidden? In the undisputed sections of the Asc. Isa. the Beloved’s identity is hidden by means of changing his appearance. In the disputed passage, however, we appear to see quite a leap: the Beloved does things that must surely reveal his identity but miraculously God somehow stops people from “knowing who he is”.
Another problematic detail is in 11:21
20. In Jerusalem indeed I saw Him being crucified on a tree:
21. And likewise after the third day rise again and remain days.
If Jesus is shown to have “remained days” on earth after his resurrection then we have another contradiction with the stated theme of the larger Asc. Isa.. The “Beloved” is said in the larger Asc. Isa. to descend for the purpose of defeating the power of death. His death is his ticket of access to Hades. Once done, he is said to ascend back to the seventh heaven. Conclusion: there is no place for introducing a longer stay on earth after his resurrection. Such a detail must be an addition from later orthodoxy. It flies in the face of the otherwise stated point of the Beloved’s descent, death and return in the Asc. Isa..
Such are more reasons James Barlow advances in this instance for interpolation. If I have misrepresented the point I would appreciate a correction. Barlow suggests that Charles appeals to orthodox faith as the measure of authenticity: when Charles expresses dissatisfaction that the shorter version of Asc. Isa. contains no details of the crucifixion, descent to Sheol and resurrection on the third day, he is arguing in a pious circle. That is, he cannot accept an original story that lacks what he thinks should be in it.
Further, we read in the last line of this disputed passage, v.22
and I saw when He sent out the Twelve Apostles and ascended.
James Barlow suggests that this detail is surely late. In our Gospel of Mark we read that Jesus sent out the Twelve very early in his career, in chapter 3, not after his death. In the book of Acts the Twelve are “sent out” by being commanded to remain in Jerusalem.
So there is clearly room for doubt about the authenticity of the pocket gospel’s authenticity.
Are there counter-reasons to think that the passage is original?

 Some Jesus mythicists, following Earl Doherty and Richard Carrier, have taken a special interest in the Ascension of Isaiah [Asc. Isa.], an early Christian text that has been used to support (not establish, as some critics have asserted) the argument that Jesus was in an early stage of tradition believed to have been crucified by demons in the firmament above the earth. Fundamental to this interpretation of the Asc. Isa. is the view proposed by some mainstream scholars that a passage describing Jesus being born on earth and finally crucified on earth in the text is a late insertion. Manuscript and some textual evidence are cited in support of this view. That passage is 11:2-22. It speaks of the virgin Mary, her husband Joseph, a mysterious birth of Jesus and Jesus suckling at Mary’s breast, a later time when Jesus performs miracles and so arouses the envy of ruling demons, and of those demons stirring up hatred against him to the point where people crucify him on a tree in Jerusalem. All the while Jesus’ true identity as the “Beloved” from God in the seventh heaven is hidden from the spirit and human realms.
Some Jesus mythicists, following Earl Doherty and Richard Carrier, have taken a special interest in the Ascension of Isaiah [Asc. Isa.], an early Christian text that has been used to support (not establish, as some critics have asserted) the argument that Jesus was in an early stage of tradition believed to have been crucified by demons in the firmament above the earth. Fundamental to this interpretation of the Asc. Isa. is the view proposed by some mainstream scholars that a passage describing Jesus being born on earth and finally crucified on earth in the text is a late insertion. Manuscript and some textual evidence are cited in support of this view. That passage is 11:2-22. It speaks of the virgin Mary, her husband Joseph, a mysterious birth of Jesus and Jesus suckling at Mary’s breast, a later time when Jesus performs miracles and so arouses the envy of ruling demons, and of those demons stirring up hatred against him to the point where people crucify him on a tree in Jerusalem. All the while Jesus’ true identity as the “Beloved” from God in the seventh heaven is hidden from the spirit and human realms.
I have long agreed with those who have shown why we should think that that passage, sometimes called “the pocket gospel”, was not an original part of the Asc. Isa.. A number of manuscripts of the text do not have it. Has not the tendency of mythical development been to elaborate rather than excise earlier traditions? If so, surely the simplest explanation is that the passage was a later addition to the story.
This is a difficult document to analyze in any exact fashion, since the several surviving manuscripts differ considerably in wording, phrases and even whole sections. It has been subjected to much editing in a complicated and uncertain pattern of revision. Many of its elements are quite revealing, not the least for the picture they disclose of the evolution of thought about the descending Son and his role. That picture indicates that in its earlier strata, the Vision speaks of a divine Son who operates entirely in the supernatural realm. (Doherty, JNGNM, 119)
I have come to have doubts, however. I have long been in two minds over various hypotheses that Jesus was crucified by demons in the firmament (Couchoud, Doherty, Carrier). There are several reasons to think that the earliest Jesus myth is the most obvious orthodox one: that Jesus came from heaven, was crucified on earth, descended beneath the earth, then ascended back to heaven. I can address the reasons later.
In this post I want to begin tackling some of the trickier questions surrounding the Ascension of Isaiah. The person I have to thank for this review of my thinking is James Barlow who, I understand, has Masters and Doctoral degrees in Divinity and until his retirement belonged to the Anglican clergy. I have been perusing on and off for over a year a detailed commentary he prepared on the Vision chapters (6 to 11) of the Asc. Isa.
JB presents a very detailed case for the Asc. Isa. being behind some of Paul’s statements in 1 Corinthians and for the pocket gospel being an interpolation into the original Asc. Isa..
1 Cor. 2:6-9
We do, however, speak a message of wisdom among the mature, but not the wisdom of this age or of the rulers of this age, who are coming to nothing. 7 No, we declare God’s wisdom, a mystery that has been hidden and that God destined for our glory before time began. 8 None of the rulers of this age understood it, for if they had, they would not have crucified the Lord of glory. 9 However, as it is written:
“What no eye has seen,
what no ear has heard,
and what no human mind has conceived”—
the things God has prepared for those who love him—
1 Cor. 15:3-4
For what I received I passed on to you as of first importance: that Christ died for our sins according to the Scriptures,4 that he was buried, that he was raised on the third day according to the Scriptures.
“As it is written” and “according to the Scriptures” should not be casually assumed to refer to the “Old Testament”. A very reasonable case can be made that Paul has less orthodox writings (viz the Asc. Isa.) in mind. I won’t take up that question now, either.
But because I know the Asc. Isa. has a particular interest for many readers of Vridar, I want to begin here to think through some of the reasons for concluding that the “pocket gospel” of 11:2-22 was not part of the original Ascension of Isaiah. I have begun to suspect it might be original after all. Continue reading “Ascension of Isaiah: Questions”

Continuing my outline of Celine-Marie Pascale’s article The Weaponization of Language. Wherever possible hyperlinks take you to the direct source online. Hopefully, interested readers will find leads to many other relevant sources here either by direct or indirect links.
Celine-Marie Pascale surveys the way disinformation enters our everyday discourse, making “ordinary people” “unwitting tools of right-wing movements”.
Despite its [=the great replacement theory] French origins, the ISD’s analysis has revealed that the theory is becoming more prevalent internationally, with English-speaking countries now accounting for 33% of online discussion.
Julia Ebner, co-author of the report at ISD, said: “It’s shocking to see the extent to which extreme-right concepts such as the ‘great replacement’ theory and calls for ‘remigration’ have entered mainstream political discourse and are now referenced by politicians who head states and sit in parliaments.”
(Iqbal and Townsend)
Weaponized language is a powerful form of symbolic violence that tills the soil for physical violence. Following the Christchurch massacre, the Institute for Strategic Dialogue identified 10 Twitter accounts that were most influential in propagating the idea that white people are under attack; eight of these were in France, one belonged to the extreme right site Defend Europa, and the other belonged to Donald Trump (Iqbal and Townsend, 2019). Weaponized language has preceded and accompanied every act of collective violence. In mundane discourses weaponized language normalizes hate and hate groups through purportedly ordinary language.
(Pascale, 909)
In the United States, for example, the term ‘illegal alien’ is often used to dehumanize those seeking asylum. Political and media discourses often refer to ‘chain migration,’ when in fact they are talking about family reunification. Many in the United States use the term ‘chain migration’ simply because they are repeating the only phrasing that they have ever heard. However, we come to see the world as we learn to name and describe it. Metaphors and linguistic frames seep into everyday discourse and gradually become part of a worldview. In every country, the racialized citizen is an illegitimate citizen whose welfare is precarious. Trump’s anti-Muslim and anti-Latino hate speech is directly correlated with increased hate crimes against Muslims and Latinos in the United States (Beutel, 2018).
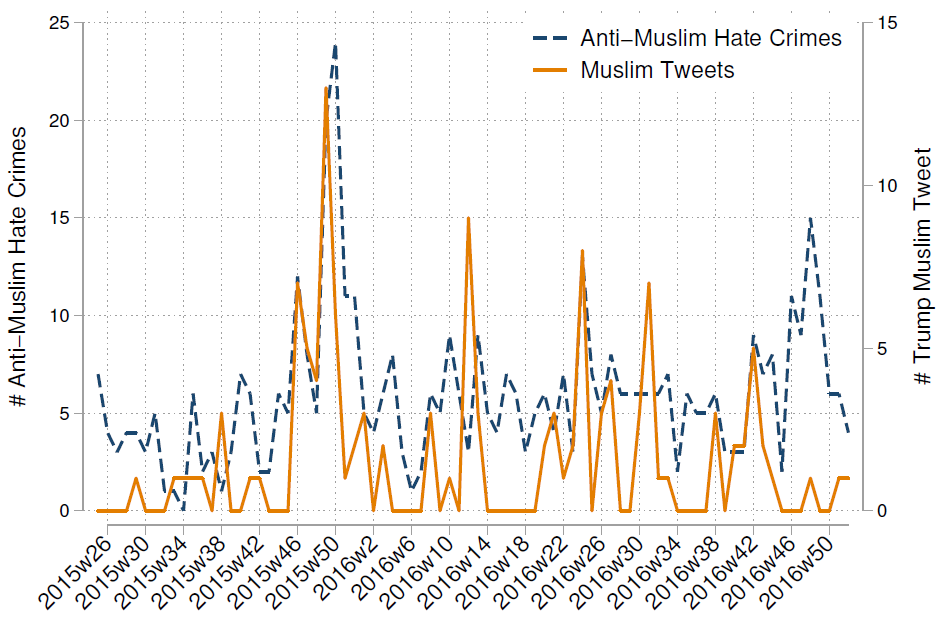
Pascale notes two other extremist trends in the U.S.:
Such attacks on children have been made possible by the very intentional linguist practices that preceded these actions. Trump’s Twitter account has been identified by the Institute for Strategic Dialogue as one of the 10 most influential accounts in the world for propagating the extreme right-wing paranoia that white people are being eliminated through migration and violence (Iqbal and Townsend, 2019).
. . . we are familiar with the practices of ‘othering’ that devalues people and excludes them from deserving empathetic consideration. A lack of empathy is easily leveraged into a willingness to disregard harm done to those who are ‘othered,’ and then escalated into a willingness to inflict harm upon them, which is often rationalized as selfprotection. Ultimately, ‘othering’ blames victims for the suffering inflicted upon them.
(Pascale, 909)
It’s not only the U.S. and Europe, of course. It’s happening throughout the world. Racial slurs have preceded genocidal acts throughout history and up to today (e.g. Buddhist Myanmar’s purging of Muslim Rohoginyas).
Nationalism depends upon slurs that are used to construct groups of people as being less than human, as being potentially violent predators, and as deserving any harsh treatment they might receive. Slurs have been used to create dehumanized enemies throughout time. It is the essential first step that justifies physical violence.
(Pascale, 910)
Hate movements have learned to rebrand themselves so they can attract larger support.
White supremacists have rebranded themselves as the “alt-right”, “as if they are a legitimate party with a platform beyond white supremacy.” (Pascale, 910) Alt-right is a “usefully” vague term that found a web and social media revival in 2015:
While the nationalist, white identity-obsessed core of the alright remained the same, the nature of its supporters began to shift. Alice Marwick and Becca Lewis chronicle this evolution in their 2016 report on online misinformation and disinformation. They explain that the “accommodatingly imprecise” alt-right label had, by the 2016 election, been embraced by, or at least was being used to describe, a range of “conspiracy theorists, techno-libertarians, white nationalists, Men’s Rights advocates, trolls, anti-feminists, anti-immigration activists, and bored young people” (Marwick and Lewis, 3). The reemergence of the alt-right also coincided with, and indeed was driven by, a rising tide of global far-right extremism.
(Philips, 4)
The same report demonstrates through detailed media citation and sentence topic analyses that the far-right articles gained far more mass media coverage than their small numbers would predict. Mainstream media was the booster for extremist right-wing talking points merely as a result of noting and commenting on them. Breitbart and other extremist blogs had a relatively small audience but nonetheless were able to “set the mainstream agenda” with the help of mainstream media:
These [extremist] media, instead, depended on the signal boosting power provided by center-left establishment publications like The New York Times, The Washington Post, and CNN.com to ensure that their messages would spread to a national, or even global, audience. That’s how Pepe the Frog lept onto the public stage. That’s how Donald Trump Jr.’s Instagram post became a national news story, and ultimately, a talking point in two presidential candidates’ campaigns. That’s how many Americans first heard the term “alt-right.”
(Philips, 6)
We also know how others such as religious fundamentalists and those who call themselves conservatives deploy language that justifies hatred towards other religious, racial or unorthodox gender-identity groups.
There is debate, of course, and challenges are mounted. But the challenges work both ways as one group seeks to subvert another: Black Lives Matter is met with All Lives Matter; immigrant Dreamers are met with We Are All Dreamers.
The most serious stage of the problem is when people can no longer find other positive or neutral words to frame the issues that are dividing society.
One group of people who study these sorts of phenomena, how societies work, how different groups react and respond to adverse situations and each other, are the sociologists, the political scientists, the historians, the anthropologists, the psychologists. These academics are the ones who are coming under regular attack as “left-wing”, “liberal”, just as serious climate scientists, and now even many medical scientists, are being widely attacked by authoritarian and right-wing extremists. Meanwhile, the media reporting on these attacks is itself branded “fake news”.
It would be nice to think that merely responding with “fact-checking” would be the answer. Unfortunately, if it were so simple we would not be in this state of affairs now:
Global circumstances would seem to invite social sciences in general, and sociologists in particular, to fight back by entrenching ourselves in the world of objective facts. This path is important and perhaps irresistible when politicians and media openly make statements that are certifiably false. However, a retrenchment of empiricism will not deliver us from this historical moment, just as it did not prevent it from arriving. Indeed, it is often government efforts to slide facts that lead to the preposterous logic they present to the public. As Montaigne reminds us, falsehood is not the opposite of truth. Unbound by logic and fact, those willing to weaponize language have boundless possibilities. The four-fold strategy of right-wing authoritarianism leveraged through censorship, propaganda, disinformation, and mundane discourse can itself debilitate resistance, as it is intended.
(Pascale, 911)
Beutel, Alejandro. 2018. “How Trump’s Nativist Tweets Overlap with Anti-Muslim and Anti-Latino Hate Crimes.” Southern Poverty Law Center. May 18, 2018. https://www.splcenter.org/hatewatch/2018/05/18/how-trump%E2%80%99s-nativist-tweets-overlap-anti-muslim-and-anti-latino-hate-crimes.
Iqbal, Nosheen, and Mark Townsend. 2019. “Christchurch Mosque Killer’s Theories Seeping into Mainstream, Report Warns.” The Observer, July 7, 2019, sec. World news. https://www.theguardian.com/world/2019/jul/07/christchurch-mosque-killer-ideas-mainstream-social-media.
Klemperer, Victor. 2013. Language of the Third Reich: LTI: Lingua Tertii Imperii. London ; New York: Bloomsbury Academic.
Marwick, Alice, and Rebecca Lewis. 2017. “Media Manipulation and Disinformation Online.” Data & Society Research Institute. https://datasociety.net/library/media-manipulation-and-disinfo-online/.
Pascale, Celine-Marie. 2019. “The Weaponization of Language: Discourses of Rising Right-Wing Authoritarianism.” Current Sociology Review 67 (6): 898–917. https://doi.org/10.1177/0011392119869963.
Phillips, Whitney. 2018. “The Oxygen of Amplification: Better Practices for Reporting on Extremists, Antagonists, and Manipulators.” Data & Society Research Institute. http://datasociety.net/output/oxygen-of-amplification/.

Here we look at
a. the visions and rejoicing surrounding the birth of Jesus
b. the shepherds, the magi
c. massacre of the innocents
d. flight to and return from Egypt
e. Jesus twelve years of age in the temple
Future posts will continue this series.
|
The table is primarily a translation and slight modification of pages 183-226 of Nanine Charbonnel’s Jésus-Christ, sublime figure de paper. All posts archived here.
|

I’ve updated our archives to include an annotated page of links to all Vridar posts on the Nazareth question. Most are about the archaeology of the early first century period, but some address other questions such as the historical likelihood of Jesus being identified as “from Nazareth” and the supposed embarrassment behind the authors of the gospels of Matthew and Luke creating different narratives to explain how Nazareth entered the life of Jesus.
Check the right-hand column here and look under ARCHIVES by TOPIC. Look fo Nazareth under that heading.

This post questions the authenticity of the section in Paul’s writings where we read that “rulers of this age” crucified “the Lord of glory” followed by a passage said to be a citation of Scripture but that appears only elsewhere in the Ascension of Isaiah. The arguments for interpolation are derived from William O. Walker Jr’s chapter 6 of Interpolations in the Pauline Letters.
6 We speak wisdom among those who are perfect, although it is not a wisdom belonging to this world, nor to the governing powers [rulers] of this world [age], which are being brought to nothing,
7 but we speak God’s wisdom in a mystery, the hidden wisdom which God purposed before the worlds (or: ages), with a view to our glory.
8 This wisdom none of the governing powers [rulers] of this world (-age) has known. For if they had recognized it, they would not have crucified the Lord of glory.
9 But as it is written, “Things that no eye has seen and no ear has heard and that never entered into any man’s heart, all the things that God has prepared for those who love him.”
10 For to us God has revealed them through the Spirit. For the Spirit explores all things, including even the depths of God.
11 For who among men knows what a man is but the man’s own spirit within him? In the same way no one has recognized what God is but the Spirit of God.
12 We, however, have received not the spirit of the world, but the Spirit that comes from God, so that we may know what has been bestowed upon us by God.
13 And it is also of this that we speak, not in words taught us by human wisdom, but in words taught us by the Spirit, interpreting spiritual things in spiritual terms.
14 The unspiritual (“psychical”) man, however, does not receive the things of God’s Spirit. For they are foolishness in his eyes and he cannot recognize them, because they are (or: must be) spiritually interpreted.
15 The spiritual man, however, judges all things, but is not himself subject to anyone’s judgment.
16 For “who has discerned the mind of the Lord, so as to instruct him?” We, however, have the Spirit of Christ.
(Based on Conzelmann’s translation)

For readers impatient to get the main overview, here is a crude list of reasons some scholars have suggested the passage was not originally composed by Paul:
(Walker’s summary of Widman’s discussion: Widmann, Martin, “I Kor 2 6-16: Ein Einspruch gegen Paulus”, ZNW 70 (1979), pp. 44-53.)
Conzelmann writes in his commentary (p. 57),
The section 2:6-16 stands out from its context both in style and in content. It presents a self-contained idea, a commonplace of “wisdom.” It is a contradiction of his previous statements when Paul now announces after all a positive, undialectical possibility of cultivating a wisdom of the “perfect.”
Walker summarizes (p. 128) E. Earle Ellis’s view of the evidence for a non-Pauline origin:
On the basis of such evidence, Ellis concludes that “on balance, 1 Cor. 2.6-16 is probably a pre-formed piece that Paul has employed and adapted to its present context”.
Walker thus points out three possibilities:
Walker argues for #3. In doing so he addresses the counter-claims of Jerome Murphy-O’Connor who concludes that the passage is indeed by Paul (Interpolations in 1 Corinthians – link is to JSTOR article).
Some biblical scholars insist that we cannot make a serious case for interpolations unless we have anomalous manuscript evidence that physically demonstrates variations in editing lines. This is essentially an ostrich argument. The earliest manuscripts we have are those produced by the winners of the theological wars. We know editors fought their battles by modifying source texts. This state of affairs is not unique to the biblical texts since it is well-known that in other ancient literature interpolations were very common, and a problem that even ancient custodians (as in the Alexandrian Library) confronted. (See the Interpolations posts for additional discussion.)
There is an abrupt shift at verse 6 Continue reading ““Rulers of this Age” as part of an Interpolation into 1 Corinthians”

Continuing my outline of Celine-Marie Pascale’s article The Weaponization of Language. Wherever possible hyperlinks take you to the direct source online.
Stalin coined the word ‘dezinformatsiya’ in 1923 “to describe false information spread systematically through media and public announcements to intentionally confuse or mislead publics.” What is of particular interest at this time, however, is the use of the term “fake news” to “decry reality as fake”. Examples are cited in relation to Syria, Myanmar, Spain, Venezuela, and no doubt we can all think of many more.
In these examples, the charge of ‘fake news’ is a form of disinformation in itself. Governments are using the charge of ‘fake news’ to reshape reality as they attack information and people that they want to discredit. Sherine, one of Egypt’s most famous singers, jokingly implied it was not safe to drink from the Nile and was arrested and sentenced to six months in jail for insulting the country by ‘spreading fake news’ (BBC, 2018). As is evident in these examples, the charge of ‘fake news’ is levied by government leaders to dismiss or to attack people and ideas that are verifiably true.
(Pascale, 905f. Italics original; bolding added)

From the Schwartz article linked in the above quote:
“These governments, they’re pushing the boundaries of what it’s possible to get away with in terms of controlling their national media,” said Steve Coll, dean of the Columbia Journalism School, “and there’s no question that this kind of speech makes it easier for them to stretch those boundaries.”
White House press secretary Sarah Huckabee Sanders pushed back against the idea that Trump bears responsibility. “This story is really ridiculous,” she said in an email. “The president isn’t against free speech but we do think reporting should be accurate.”
The spread of the phrase has come against a backdrop of rising violence and persecution against journalists . . . .
Trump’s go-to insult has become such a touchstone that members of far-right groups or political parties in countries like the Netherlands or Germany often write “fake news” in English in their tweets, said Cas Mudde, an international affairs professor at the University of Georgia.
“I have seen it particularly in social media used by radical right leaders who have been clearly influenced by Trump’s use,” he said. “Even if they have a tweet in Dutch, there will be a hashtag #fakenews in it.”
Returning to Pascale:
Disinformation campaigns are designed to consolidate power by provoking reactionary responses that sustain epidemics of social unrest. For example, the US intelligence community pummeled Chile with disinformation in order to unseat the democratically elected President Salvador Allende and install Augosto Pinochet (Carter, 2014). Recently, researchers have documented that Russia targeted specific racial groups in the United States with more than 80,000 posts and thousands of ads that mimicked the style of Black Lives Matter activists in order to stoke racialized conflict and unrest (Associated Press, 2018). Each of these postings proliferated through social media re-postings.
Disinformation might contain complete falsehoods or partial truths, or it might distort reality by representing an unusual circumstance as a common one. Disinformation campaigns also often incorporate conspiracy theories which delegitimize mainstream media and are used to target people and ideas. For example, Nazi ideology, rife with conspiracies theories regarding Jews, is one of many examples of a disinformation campaign. Jewish conspiracy theories remain today. In 2018 Hungarian Prime Minister Viktor Orbán forced the closing of the Central European University (CEU), a private university funded by George Soros, an American of Hungarian and Jewish origin. Orbán, who has promised to defend his Christian homeland, claimed the CEU was part of a plan by Soros to flood Hungary with non-Christian immigrants (Stanley, 2018).
Conspiracy theories are a complete subject of their own and I hope to be posting soon on some new academic publications that have come out these past two years addressing their nature, reasons, and function in today’s political climate.
Meanwhile,
“The president’s proclivity to twist data and fabricate stories is on full display at his rallies. He has his greatest hits: 120 times he had falsely said he passed the biggest tax cut in history, 80 times he has asserted that the U.S. economy today is the best in history . . .
“Nearly 25 times, he has claimed that Supreme Court nominee Brett Kavanaugh was No. 1 in his class at Yale University or at Yale Law School. . . .
“This is one of those facts that can be easily checked with a Google search, yet the president persists with his falsehood.”
(Kessler et al., 2018)
Trump is known to have made the same false claim more than 120 times (Kessler et al., 2018). Donald Trump seems to be drawing from Lenin’s old aphorism that a lie told often enough becomes the truth. However, in the internet age Lenin’s aphorism could be updated to ‘If you make it trend, you make it true’ (DiResta, 2018). Truth and politics have never been on the best of terms (Arendt, 1967 link is to PDF) but we have entered new territory. It isn’t only the numbers of lies that pose a threat.
Consider that Trump’s lies are different in kind, not just in quantity, from typical people. When ordinary people lie, we orient toward the truth in order to make our lies seem plausible (Carson, 2016; Frankfurt, 2005– link is to PDF). We want our lies to been seen as being true; this is the nature of deceit. Ordinary people craft lies with an eye to preventing ourselves from being exposed for having lied. This has not been the case for Trump, whose lies are not masked. Indeed, he openly bragged about lying to the Canadian Prime Minister about trade deficits. Trump is not attempting to get away with a lie. Rather, Trump’s lies convey an impression that he wields unconstrained power: he can say whatever he wants to say, and the world just has to take it. Perhaps it is even a little sweeter for him, when people know he is lying but can do nothing about it. To the extent that he seems to have impunity it is because he does not stand alone; he is part of a comprehensive system that brought him to power and ensures his survival. Even when media identify lies, a significant part of the population does not care – indeed he is part of a cohort of world leaders who adopt a very similar approach. Trump’s communication has been successful – even while those of us wedded to facts may think otherwise. Efforts to demonstrate the falsity of his claims are important yet never adequate. This is precisely why we, as sociologists, must pay attention to the use of language – not just matters of fact.
Disinformation campaigns online are a powerful, effective, and inexpensive means to generate political and social chaos. Disinformation and propaganda working together do more than create factions and tensions between them. They place factual reality itself at risk. The greatest danger is not that lies will be accepted as truth and truth defamed as lies, but that ‘the sense by which we take our bearings in the real world – and the category of truth vs. falsehood is among the mental means to this end – is being destroyed’ (Arendt, 1967: 50). Reality itself becomes more contingent and less objectively real. Reasoned debate is replaced by emotional spectacles.
(Pascale, 908)
Next: Mundane Discourse….
Omg — after I posted the above I turned to twitter and what did I see there but this as if right on cue. . . . Continue reading “The Weaponization of Language (Part 4) – Disinformation and fake news”

Another fascinating program, King Arthur’s Britain: Truth Unearthed
As a boy, I read in children’s books that after the Romans evacuated Britain early in the fifth century the indigenous peoples fell into warlike anarchy and only came together again under the leadership of King Arthur to confront the new invaders from Europe, the Angles, Saxons and Jutes, who had driven the Britons back to the western part of the isles.

Just like the biblical story of King David, I am almost certain that the literary legends are fantasy. Archaeology and DNA, in their current state, appear to leave no room for such scenarios of mass invasions, displacements or a heroic King Arthur rising to save such a day.
Evidence datapoint #1: of the thousands of human skeletons from the period of the fifth and sixth centuries, only 2% have signs of sharp cutting blows that indicate a violent end.
Evidence datapoint #2: widespread and extensive archaeological digs indicate open farming settlements, not fortresses.
Evidence datapoint #3: Jewellery of a Saxon cruciform with a skeleton was long assumed to have been an indicator the person was a Saxon; but new x-ray technology applied to such jewellery shows that it was overlaid with a glass-based enamel that was characteristic of the crafts of the Britons and nowhere found in Europe. It thus appears that such jewellery points to Saxon influence of the design upon the crafts of the native Britons. We cannot assume that the Saxons displaced the Britons in the east.
Evidence datapoint #4: Ancient DNA tests show that some skeletons of the period were the products of intermarriage of Saxons and Britons.
Evidence datapoint #5: Modern DNA tests show a homogeneity of DNA mix among the population of central and western England; this area experienced the most concentrated Roman settlement and was easily traversable through Roman roads here. Other parts of the British Isles show less integrated DNA, suggesting that over the centuries these areas (in the west and south-west) integrated less with European settlers. The thorough mix of DNA in the central and east parts of England demonstrate an integration of populations, of Angles and Saxons with the Britons, and not a replacement of one population by the other.
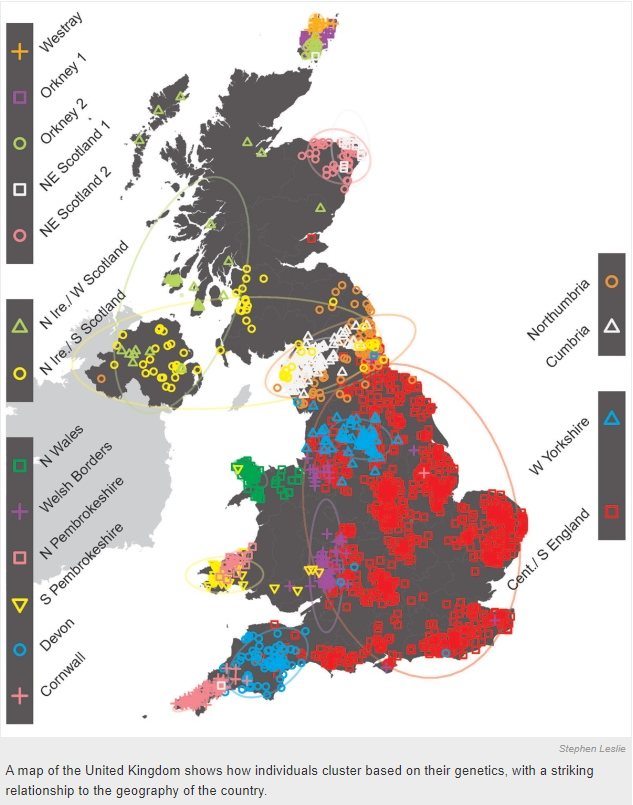
Evidence datapoint #6: Pottery finds point to Britons (who had a major centre at Tintagel) were trading extensively by sea with Spain, North Africa, through to Anatolia or where modern Turkey is, all through the Byzantine era; meanwhile the eastern part of Britain was trading most with northern and north-western Europe, the Scandinavian and north European areas from where they had originated.
Conclusion: There were no population displacements with the arrival of the Angles, Saxons and Jutes. Rather, these newcomers probably set up in their self-contained communities at first but over time came to integrate with the indigenous population. It was more like the settlement of America, Italian Americans, German Americans, Black Americans, each coming in in their own “waves”.
There is no evidence of breakdown into violent anarchy. The two sides of Britain, west and east, appear to have been quite prosperous regions. There is even evidence of literacy among them. There was no scenario that fits the glorious, superhuman tales of King Arthur, happily.
A monk, Gilgal, from the supposed time of King Arthur, writes diatribes against the sins of the Britons and how the Saxon invasions were God’s punishment on them, but he makes no mention of Arthur and we have no way of testing his image of the times. He appears more devoted to writing “godly polemics”.
Geoffrey of Monmouth, our first recorder of King Arthur’s exploits, wrote in the twelfth century. Our material evidence, clay, rock and DNA, suggests his history is fantasy.
The question to ask is what was it about Geoffrey’s day that led him to write about a saviour king in troubled times.

Scott, Kenny. 2018. King Arthur’s Britain: Truth Unearthed. BBC. https://www.sbs.com.au/ondemand/video/1419920963667/king-arthurs-britain-truth-unearthed. [Presented by Dr Alice Roberts]
Callaway, Ewen. 2015. “Uk Mapped Out by Genetic Ancestry.” Nature News. Accessed May 18, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature.2015.17136.
Leslie, Stephen, Bruce Winney, Garrett Hellenthal, Dan Davison, Abdelhamid Boumertit, Tammy Day, Katarzyna Hutnik, et al. 2015. “The Fine-Scale Genetic Structure of the British Population.” Nature 519 (7543): 309–14. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14230.

Continuing in this post with my outline of Celine-Marie Pascale’s article The Weaponization of Language. This post addresses her section on a favourite topic of mine, one that I’ve posted many times about, Propaganda. I’ve fleshed out some of Pascale’s points by going back to her citations and quoting directly from them. (Other links point to the online articles themselves where available.)
Propaganda might be most commonly associated with the effort of governments to manipulate information and sentiments to gain public support for specific agendas (Messeryly, 2015). In the United States, the term propaganda has been used to characterize the kinds of interventions advanced by the Soviet Union. When the same critical lens is turned toward modern liberal political democracies, propaganda is often referred to as manufacturing consent (Ellul, 1973; Herman and Chomsky, 2002). In the United States it has been used to intensify capitalist impulses. Sigmund Freud’s nephew, Edward Bernays, developed propaganda (which he referred to as public relations) as a means to compel people to buy products they did not need. Propaganda’s sole task is to shape desires and dispositions. Through propaganda Bernays also pushed back on all forms of regulation and in the US made free-market capitalism synonymous with democracy. Bernays’ propaganda machine was so effective that it inspired Joseph Goebbels, the Reich Minister of Propaganda in Nazi Germany (Curtis, 2002).

Do click on and view that Curtis, 2002 link at the end of the above paragraph if you haven’t already seen it. It is a BBC documentary by Adam Curtis, 58 minutes long, and part 1 of a series of 4 that survey the way government and business have used the theories of Sigmund Freud to control the masses in an age of “democracy”. I’ve covered aspects of what he addresses in other posts here, in particular the influence of Freud’s nephew, Edward Bernays. Bernays, we learn from a close family member in the doco, despised the masses, thought of them as “fools”. No wonder, when it shows how he became extremely wealthy by showing governments and businesses how to manipulate them.
But back to our Pascale article and to begin with the more obvious:
Some tools frequently used by propaganda are
We have come to expect the abundance of “slogans, images, and catchphrases” at election time.
With consistent exposure over time, propaganda becomes a language that thinks for you (Klemperer, 2013).
I looked up the Klemperer reference. Here are a few extracts from Victor Klemperer’s The Language of the Third Reich:
Continue reading “The Weaponization of Language (Part 3) – Propaganda”

Here we look at
a. the announcement to the parents of John the Baptist;
b. the heralding role of John the Baptist.
Future posts will continue this series.

From The Guardian the day after I posted The Weaponization of Language (Part 2): Censorship
.
As Donald Trump agitates for the US to reopen, the American right appears to have found a novel way to deal with the rising coronavirus death toll: deny it altogether.
Top Trump officials, huddled in the White House, itself the subject of a coronavirus outbreak, have according to reports begun questioning the number of deaths – and the president is among the skeptics.
It’s a handy thought process for an administration desperate to send Americans back to work even as deaths from the virus rise each day, with marked surges in some traditionally Republican states.
. . . .
Worryingly, the disinformation push seems to be working. An Axios-Ipsos poll found that the death toll has become a political issue, 40% of Republicans believing fewer Americans are dying from coronavirus than the official toll says.
A separate study, published at the end of April, revealed the stark consequences of prominent figures underplaying the impact of Covid-19. A group of researchers tracked the spread of coronavirus among viewers of Sean Hannity’s Fox News show, after Hannity spent weeks downplaying the threat.
“Greater exposure to Hannity,” the researchers wrote, “leads to a greater number of Covid-19 cases and deaths.”
.