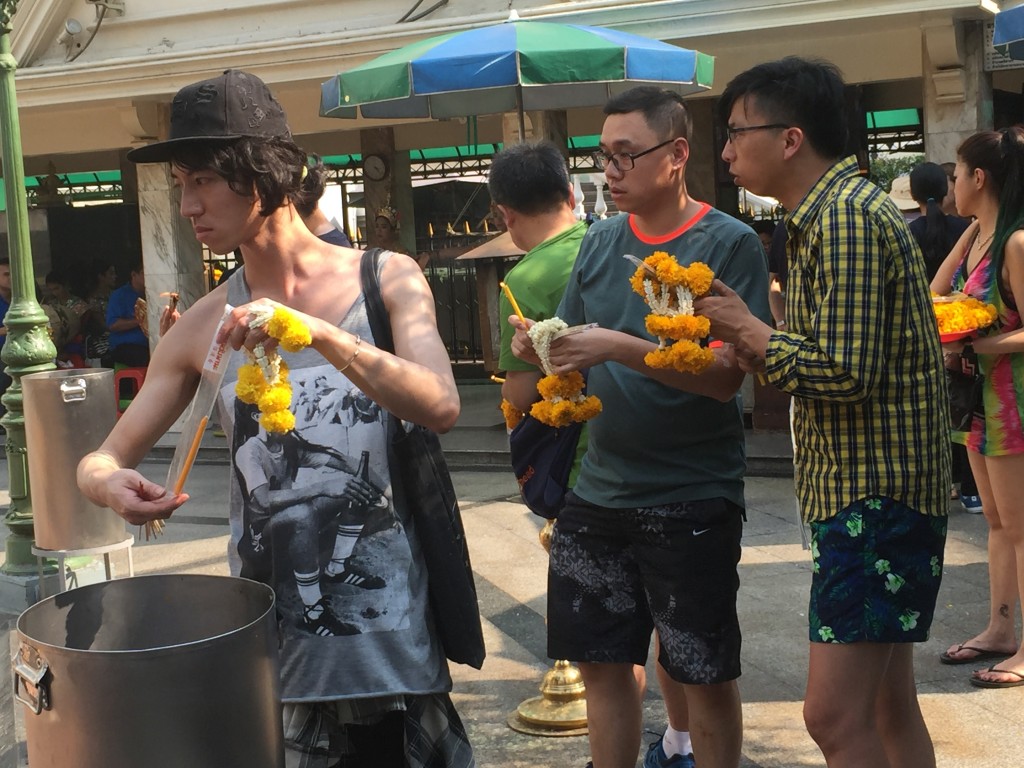
Raphael Lataster in Jesus Did Not Exist: A Debate Among Atheists shows readers that one does not have to personally like Richard Carrier to agree and critically engage with his arguments. Lataster addresses the “stumbling block” of Carrier’s abrasive blog comments and his promotion of controversial relationships values that have made and makes it clear that in both areas he, Raphael Lataster, stands in diametric opposition to Carrier.
It is worth noting that I have no great inherent desire to promote Carrier or his work –he is certainly no friend of mine. Some of what he says and does is annoying, seemingly egotistical, and even offensive to me, and we are otherwise quite different. . . .
Nevertheless, apart from his frankness, none of this is truly relevant. The man is a rigorous logician and undertakes interesting and important research. I do not need to judge how he lives his life; nor do I wish to poison the well, especially since I am upholding him as the exemplar for the mythicist position. I only wish to highlight that our relationship is strictly professional. We are bound by the same dedication to truth, logic, and sound methodologies. (JDNE, Kindle, loc 5661-5672)
Lataster’s comments on Carrier are just an aside and not related to what this post is about.
My own stumbling block is a different one and here I post another quibble I have with both Carrier’s On the Historicity of Jesus and Lataster’s review of it. (See Carrier, Lataster and Background Knowledge Element 4: A Quibble for my previous quibble.) Don’t think from these posts that Lataster blindly follows Carrier in all his arguments, by the way. Lataster does have a few of his own criticisms. Here I am commenting where I part from them both.
Quibble #2
Carrier writes in OHJ, p 614 in relation to 1 Corinthians 1:23 (Paul’s preaching Christ crucified being a stumbling block to the Jews):
It’s worth emphasizing here that we have absolutely no evidence that any ancient Jews (much less all of them) considered the idea of exalting a slain messiah to be blasphemous or illegal or even inconceivable — that’s a modem myth. To the contrary, the evidence we do have (from the Talmud, for example) shows they had no trouble conceiving and allowing such a thing (Element 5). Nor would such a notion be foolish to pagans, who had their own dying saviors, historical (Element 43) and mythical (Element 3 1 ). So the only thing Paul could mean the Jews were stumbling over was the notion that a celestial being could be crucified — as that would indeed seem strange, and would indeed be met with requests for evidence (‘ How do you know that happened?’).
Lataster appears to support Carrier’s analysis.
Something is amiss here. A couple of things, actually. The imaginary rhetorical questions posed by the Jews would scarcely have arisen if, as is soundly argued elsewhere, Paul “knew” it happened because of revelation and scripture. Those to whom God revealed it knew it to be so just as they knew anything else God revealed to them by his spirit.
One would expect if Paul was responding to such questions he would simply have pointed to the scriptural passages that midrashically (not literally, of course) revealed the point.
Carrier supports his interpretation by pointing to the preceding verse faulting the Jews for asking for signs to prove a claim said to be divinely revealed. The Jews failed to believe Paul, Carrier argues, because Paul could produce “no sufficient signs” to prove it was God’s truth.
Again I have difficulty here. Paul also says he produced signs more abundantly than other apostles. Besides, he goes on to say that the gospel itself is a power or sign far greater than anything else. The Jews simply fail to recognize the sign.
Besides, as Carrier rightly points out,
A martyred savior was never a stumbling block to Jews nor foolish to pagans (Element 43). Nor did it require signs or mystical evidence.
Why should a martyred saviour be any more of a problem if the event occurred in a heavenly realm? Recall Daniel 7’s suggestion that the Son of Man in heaven represented the slain martyrs and how from this seed the heavenly messiah evolved into a literal figure in the heavens; and again in the Book of Hebrews the sacrifice could be reasoned quite logically as happening in heaven.
I’m more persuaded by Morton Smith’s explication of 1 Corinthians 1:23 (Was Paul Really Persecuted for Preaching a Crucified Christ?). What was the offence was not the crucifixion of the messiah itself but what this death meant. Paul was preaching salvation, adoption as an eternal son of God, by the abolition of the wall of the Law dividing Jews and Gentiles from each other and both from God himself. Now that gospel really does sound like weakness to Jews and folly to gentiles.

 Bart gets on a roll in
Bart gets on a roll in