This post relates to an earlier one on Keller here.
Timothy Keller in The Reason for God makes an astonishing claim meant to reinforce the argument that the gospels could not possibly be fictional:
The literary form of the gospels is too detailed to be legend.
Modern fiction . . . contains details and dialogue and reads like an eyewitness account. . . . In ancient times, romances, epics, or legends were high and remote — details were spare and only included if they promoted character development or drove the plot. . . . In modern novels, details are added to create the aura of realism, but that was never the case in ancient fiction.
The gospel accounts are not fiction. In Mark 4, we are told that Jesus was asleep on a cushion in the stern of a boat. In John 21 we are toldthat Peter was a hundred yards out in the water when he saw Jesus on the beach. He then jumped out of the boat and together they caught 153 fish. . . . None of these details are relevant to the plot or character development at all. If you or I were making up an exciting story about Jesus, we would include such remakrs just to fill out the story’s air of realism. But that kind of fictional writing was unknown in the first century. The only explanation for why an ancient writer would mention the cushion, the 153 fish . . . . is because the details had been retained in the eyewitnesses’ memory. (pp. 106-107 — underlining is my emphasis)
Timothy Keller has clearly never read any (or certainly very very little) ancient fiction from the Greco-Roman period spanning the time of the gospels.
Unfortunately my own collection of ancient Greek novels (spanning b.c.e. to c.e.) is back in Australia, but there is still enough translated content online to give anyone interested the ability to assess Keller’s assertion that the gospels, because they include realistic details that do not advance the plot, are unlike any ancient fiction and therefore can only be understood as records of eyewitness testimony.
More than a match for Mark’s “cushion in the boat” detail
If one wants an ancient fictional counterpart to the detail in Mark of Jesus sleeping on a cushion, how about this description concerning a famous Greek hero who went to sleep on a boat:
As he spoke he crossed the threshold, and Alkinoos sent a man to conduct him to his ship and to the sea shore. Arete also sent some maid servants with him – one with a clean shirt and cloak, another to carry his strong-box, and a third with grain and wine. When they got to the water side the crew took these things and put them on board, with all the meat and drink; but for Odysseus they spread a rug and a linen sheet on deck that he might sleep soundly in the stern of the ship. . . .Thereon, when they began rowing out to sea, Odysseus fell into a deep, sweet, and almost deathlike slumber. (Homer’s Odyssey, 13.63)
“In modern novels, details are added to create the aura of realism, but that was never the case in ancient fiction”? I submit that a spread out rug and linen sheet in the stern of a ship beats a mere cushion for realistic detail in any age.
The identities and the voyages of the Argonauts
From the ancient romance of Jason and the Argonauts in their quest for the golden fleece, by Apollonius
Book 1 of this novel (the Argonautica) begins with a list of not just 12 names who will follow the hero, Jason, but with 50 – and each of the 50 names is described with some unique detail that in most cases will have nothing whatever to do with advancing the plot. Apollonius is a master of infusing his narrative with “realistic details”. One example of his love for detail that serves no purpose other than to encourage the audience to sit back and picture the events unfolding “realistically” in their minds’ eye:
And straightway the misty land of the Pelasgians, rich in cornfields, sank out of sight, and ever speeding onward they passed the rugged sides of Pelion; and the Sepian headland sank away, and Sciathus appeared in the sea, and far off appeared Piresiae and the calm shore of Magnesia on the mainland and the tomb of Dolops; here then in the evening, as the wind blew against them, they put to land, and paying honour to him at nightfall burnt sheep as victims, while the sea was tossed by the swell: and for two days they lingered on the shore, but on the third day they put forth the ship, spreading on high the broad sail. And even now men call that beach Aphetae of Argo.
On meeting a companion
Some web filters would block much detail from Petronius’s Satyricon, but enough can be salvaged to publicly belie Keller’s fatuous claim:
After running about almost over the city, I caught sight of Giton, as it were a fog, standing at the corner of an alley close to the door of our inn, and hurried to join him. I asked my favorite whether he had got anything ready for our dinner, whereupon the lad sat down on the bed and began wiping away the tears with his thumb. Much disturbed at my favorite’s distress, I demanded what had happened. For a long time I could not drag a word out of him, not indeed till I had added threats to prayers. Then he reluctantly told me. . . .
He didn’t just see Giton, he saw him “at the corner of an alley” and “close to the door” and not just any door, but the one “of our inn”. And the two didn’t just begin to speak — that is all the plot would have required, and the character development — but he spoke while he “sat down on the bed”, etc etc etc. . . .
Can this ancient account, so rich in detail that was never the case in ancient fiction (Keller!), really have no explanation other than being derived from eyewitness testimony?
On getting off his horse
Another any reader can consult online is The Golden Ass by Lucius Apuleius. (The translation is 16th century but I have updated the spelling.)
As I fortuned to take my voyage into Thessaly, about certain affairs which I had to do (for there my ancestry by my mothers side inhabits, descended of the line of that most excellent person Plutarch, and of Sextus the Philosopher his Nephew, which is to us a great honour) and after that by much travel and great pain I had passed over the high mountains and slippery valleys, and had ridden through the cloggy fallowed fields; perceiving that my horse did wax somewhat slow, and to the intent likewise that I might repose and strengthen my self (being weary with riding) I lighted off my horse, and wiping the sweat from every part of his body, I unbridled him, and walked him softly in my hand, to the end he might piss, and ease himself of his weariness and travel: and while he went grazing freshly in the field (casting his head sometimes aside, as a token of rejoycing and gladness) I perceived a little before me two companions riding, and so I overtaking them made a third. . . .
Riding through slippery valleys, cloggy fallowed fields, wiping the sweat from the horse’s body, letting his horse have a piss, seeing its head shake from side to side. . . .
And Thomas Keller claims in a best selling religious tract that the ancients did not use realistic detail to portray fiction!
The story of Atlantis by Plato
This, by Keller’s lights, is the truest of all, since it not only recreates an ancient civilization in amazing detail, but is introduced with many assertions that it really is indeed a true story. And the richness of the detail in how the story came to be known by Critias has convinced many even today that the tale really does have a verifiable lineage. It doesn’t, of course. Plato in the same and other books regularly makes up myths to teach his philosophy.
In Timaeus it is declared of Atlantis:
Listen then, Socrates, to a tale which, though passing strange, is yet wholly true, as Solon, the wisest of the Seven, once upon a time declared.
The details are saved for a subsequent volume: Critias 114ff
. . . but it was the eldest, who, as king, always passed on the scepter to the eldest of his sons, and thus they preserved the sovereignty for many generations; and the wealth they possessed was so immense that the like had never been seen before in any royal house nor will ever easily be seen again; and they were provided with everything of which provision was needed either in the city or throughout the rest of the country. For because of their headship they had a large supply of imports from abroad, and the island itself furnished most of the requirements of daily life,—metals, to begin with, both the hard kind and the fusible kind, which are extracted by mining, and also that kind which is now known only by name but was more than a name then, there being mines of it in many places of the island,—I mean “orichalcum,” which was the most precious of the metals then known, except gold. It brought forth also in abundance all the timbers that a forest provides for the labors of carpenters; and of animals it produced a sufficiency, both of tame and wild. Moreover, it contained a very large stock of elephants; for there was an ample food-supply not only for all the other animals which haunt the marshes and lakes and rivers, or the mountains or the plains, but likewise also for this animal, which of its nature is the largest and most voracious. And in addition to all this, it produced and brought to perfection all those sweet-scented stuffs which the earth produces now, whether made of roots or herbs or trees, or of liquid gums derived from flowers or fruits. The cultivated fruit also, and the dry, which serves us for nutriment, and all the other kinds that we use for our meals—the various species of which are comprehended under the name “vegetables”— and all the produce of trees which affords liquid and solid food and unguents, and the fruit of the orchard-trees, so hard to store, which is grown for the sake of amusement and pleasure, and all the after-dinner fruits that we serve up as welcome remedies for the sufferer from repletion,—all these that hallowed island, as it lay then beneath the sun, produced in marvellous beauty and endless abundance. And thus, receiving from the earth all these products, they furnished forth their temples and royal dwellings, their harbors and their docks, and all the rest of their country, ordering all in the fashion following.
First of all they bridged over the circles of sea which surrounded the ancient metropolis, making thereby a road towards and from the royal palace. And they had built the palace at the very beginning where the settlement was first made by their God and their ancestors; and as each king received it from his predecessor, he added to its adornment and did all he could to surpass the king before him, until finally they made of it an abode amazing to behold for the magnitude and beauty of its workmanship. For, beginning at the sea, they bored a channel right through to the outermost circle, which was three plethra in breadth, one hundred feet in depth, and fifty stades in length; and thus they made the entrance to it from the sea like that to a harbor by opening out a mouth large enough for the greatest ships to sail through. Moreover, through the circles of land, which divided those of sea, over against the bridges they opened out a channel leading from circle to circle, large enough to give passage to a single trireme; and this they roofed over above so that the sea-way was subterranean; for the lips of the landcircles were raised a sufficient height above the level of the sea. The greatest of the circles into which a boring was made for the sea was three stades in breadth, and the circle of land next to it was of equal breadth; and of the second pair of circles that of water was two stades in breadth and that of dry land equal again to the preceding one of water; and the circle which ran round the central island itself was of a stade’s breadth.
One can read the rest — the detail becoming ever more baroque — at http://tinyurl.com/ogzgg6
Given the suffeit of detail in the Atlantis account, by Timothy Keller’s claims we have far more reasons to believe Atlantis was a fact than anything in the gospels.
Letters as fiction with many touches of realism
Another form of ancient fiction was letter writing, including the creation of collections of letters to form a kind of novel. I have made my notes on Rosenmeyer’s discussion of this ancient fiction available at Ancient Epistolary Fictions on this blog.
In this work Patricia Rosenmeyer discusses in detail how budding authors were taught the art of creating realism in their fictional works by the inclusion of incidental and personal details.
The Gospel of John with novelistic features
Keller cites the 153 fish detail in the Gospel of John as reason to believe this gospel is not fiction. Scholar Jo-Ann Brant would disagree. She has written a study demonstrating the novelistic motifs throughout this Gospel.
Again I have notes from her work on this blog: Novelistic plot and motifs in the Gospel of John.
A woman weeping at a tomb
For the sake of a little irony it is appropriate to round this post off with another passage from Petronius’s Satyricon (ch.13). Here is a narrative incorporating little details that don’t seem to advance the plot or add to character development, but is about a widow weeping over her cadaverized husband in a tomb, with two crucified bodies still hanging outside nearby, and a Roman soldier. In the end the corpse is no longer found in the tomb but back on a cross.
So deep was her affliction, neither family nor friends could dissuade her from these austerities and the purpose she had formed of perishing of hunger. Even the Magistrates had to retire worsted after a last but fruitless effort. All mourned as virtually dead already a woman of such singular determination, who had already passed five days without food.
A trusty handmaid sat by her mistress’s side, mingling her tears with those of the unhappy woman, and trimming the lamp which stood in the tomb as often as it burned low. . . .
Meantime, as it fell out, the Governor of the Province ordered certain robbers to be crucified in close proximity to the vault where the matron sat bewailing the recent loss of her mate. Next night the soldier who was set to guard the crosses to prevent anyone coming and removing the robbers’ bodies to give them burial, saw a light shining among the tombs and heard the widow’s groans. . . . Accordingly he descended into the tomb, where beholding a lovely woman, he was at first confounded, thinking he saw a ghost or some supernatural vision. But presently the spectacle of the husband’s dead body lying there, and the woman’s tear-stained and nail-torn face, everything went to show him the reality, how it was a disconsolate widow unable to resign herself to the death of her helpmate. He proceeded therefore to carry his humble meal into the tomb, and to urge the fair mourner to cease her indulgence in grief so excessive, and to leave off torturing her bosom with unavailing sobs. . . . But the lady, only shocked by this offer of sympathy from a stranger’s lips, began to tear her breast with redoubled vehemence, and dragging out handfuls of her hair, she laid them on her husband’s corpse.
Given that this was written in ancient times when, supposedly, “adding little details for realistic effect was unknown”, would the little details here — the number of days without food, the mistress trimming the lamp as it burned low, the particular night in question, the good-looks of the woman, the pulling her hair out and laying it on her husband’s corpse — prove this to be an eyewitness report?
Re-reading some of the ancient fiction for this post I was reminded of another classic description of the most fabulous detail and famous throughout so much of antiquity — the description of the shield of Achilles. The details on this shield were popular enough to be emulated by Virgil for Aeneas, and by Apollonius for his cloak of Jason. A partial translation and summary of the details can be read at this Wikipedia article.
Like this:
Like Loading...
 The point of this post is to highlight, with reference to the sources, some of the less widely known beliefs among Jews around the time Christianity was emerging, and that would seem to have some resonances among Christian ideas we find in Paul and other early letters and gospels.
The point of this post is to highlight, with reference to the sources, some of the less widely known beliefs among Jews around the time Christianity was emerging, and that would seem to have some resonances among Christian ideas we find in Paul and other early letters and gospels.
 Philo was a Jewish philosopher in Egypt who died around 50 ce. Much of his literary work was an attempt to explain Jewish beliefs in the language of Greek (or Hellenistic) philosophers.
Philo was a Jewish philosopher in Egypt who died around 50 ce. Much of his literary work was an attempt to explain Jewish beliefs in the language of Greek (or Hellenistic) philosophers.
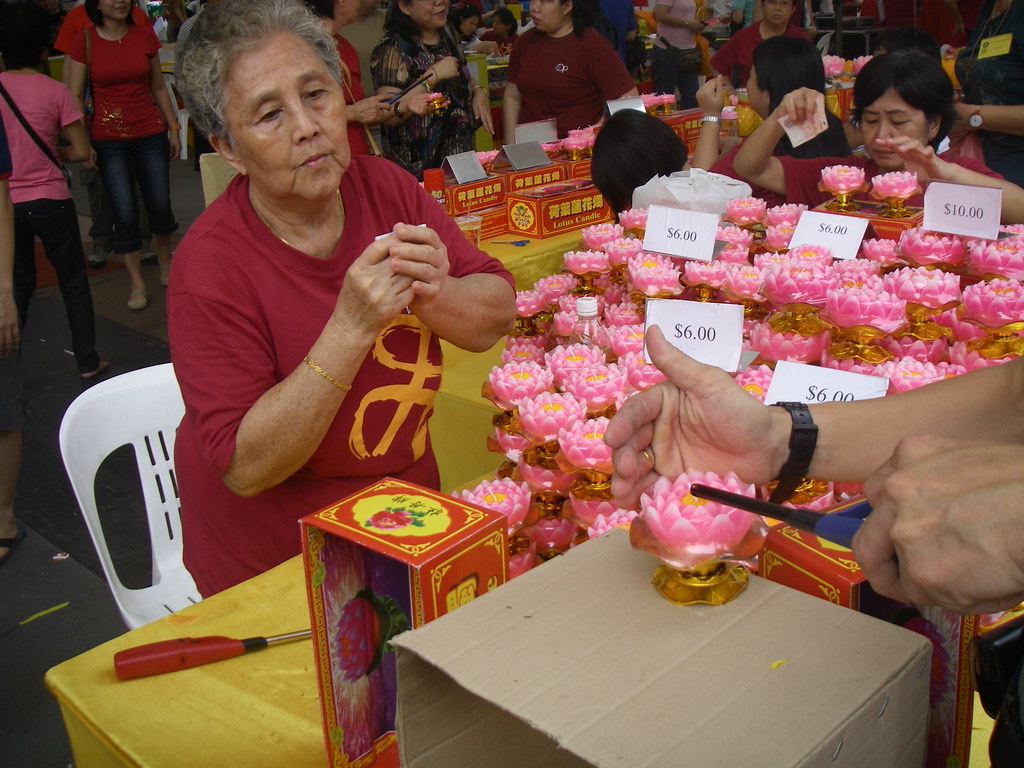


 Note the outrageous $6 price tag for a cheap lotus flower candle and fantasize Jesus descending to scare the daylights out of that greedy, money-hungry elderly lady lotus-candle-flower seller. Of course, it helps if you re-image the scene to anti-semitic stereotypes.
Note the outrageous $6 price tag for a cheap lotus flower candle and fantasize Jesus descending to scare the daylights out of that greedy, money-hungry elderly lady lotus-candle-flower seller. Of course, it helps if you re-image the scene to anti-semitic stereotypes.