The Relationship Between the Satyricon’s “Tale of the Ephesian Widow” and Texts Associated with Early Christianity.
Cabaniss, Allan; ”A Footnote to the Petronian Question”, CPh 49, 1954; pp. 98-102.
”The Satyricon and the Christian Oral Tradition,” Greek, Roman & Byzantine Studies, Vol. 3, 1960, pp. 36-9.
“The Matron of Ephesus Again: An Analysis,” Univ. of Mississippi Studies in English 3; (1962) 75-77. [Also in Liturgy and Literature: Selected Essays (Alabama, 1970).]
The Satyricon and the NT, A Satire. Liturgy and Literature, Selected Essays, University of Alabama Press, 1970, p. 72-96.
Harris, William (January 20, 1926 – February 22, 2009), Professor of Classics at Middlebury College, Middlebury, VT.
”There is no space to go into this here, but it seems clear that someone who misunderstood Christianity totally, heard of Christ’s entombment and crucifixion, and turned it into an odd form of comedy. This needs further study and discussion….”
Posted at http://community.middlebury.edu/~harris/LatinAuthors/Petronius.html.
”We should look at this from the perspective of historical evidence. If the Petronius storyline may be considered even as indirect evidence that there was an awareness, howsoever vague and transposed, of Christ’s final state, it does establish the fact that the crucifixion of Christ was becoming known in secular circles throughout the West. And it further helps document a date for Petronius (who has never been properly dated) as near the end of the first century A.D. I find this matter so strange and unparalleled by anything else we have from the early years of the first millennium, that I hesitate to propose the matter in documentable academic terms, and offer this view primarily as a suggestion for consideration. On the other hand the segments of the argument as I have outlined them seem to fit together ineluctably. It is essentially the interpretation of their meaning in a social and historical sense which gives me pause.”
Posted at http://community.middlebury.edu/~harris/Classics/crucifixion.html. Retrieved 2016/4/21.
Ramelli, Ilaria; The Ancient Novels and the New Testament: Possible Contacts; Ancient Narrative, Volume 5, Groningen; 2007; pp 41-68.
Someone may be able to persuade me otherwise, but I cannot see how Petronius’s tale of the widow of Ephesus has anything to do with Christianity. Roger Viklund has posted a bibliography of citations (see the insert box) that present the case that Petronius was somehow indebted to Christianity — presumably through garbled oral reports — or even that he constructed his account as a vicious attack on Christianity.
I cannot see it.
For those who do not know the story, here is how it begins:
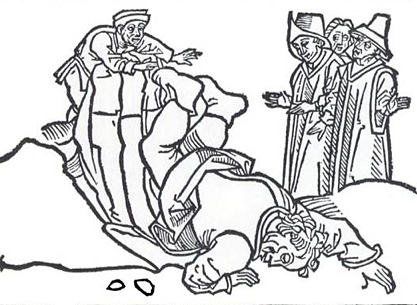
‘There was once a lady of Ephesus so famous for her fidelity to her husband that she even attracted women from neighbouring countries to come just to see her. So when she buried her husband, she was not satisfied with following him to his grave with the usual uncombed hair or beating her breast in front of the crowd, but she even accompanied the dead man into the tomb, and when the corpse was placed in the underground vault, she began watching over it from then on, weeping day and night. Neither her parents nor her relations could induce her to stop torturing herself and seeking death by starvation. Finally the magistrates were repulsed and left her, and this extraordinary example to womankind, mourned by everyone, was now spending her fifth day without food. A devoted servant sat with the ailing woman, added her tears to the lady’s grief, and refilled the lamp in the tomb whenever it began to go out. Naturally there was only one subject of conversation in the whole town: every class of people admitted there had never been such a shining example of true fidelity and love.
What we are reading here is not a reaction to (or spin-off from) Christianity but a Roman author undertaking to lampoon a very common motif in the Greco-Roman literature with which he had been familiar all his life: the ever faithful woman who would die with her deceased or departed partner rather than go on living without him. The author spells out his theme most explicitly. He is about to satirize the notion of the woman who shines as the ultimate in “true fidelity and love.”
In the words of Gian Biagio Conte in The Hidden Author: An Interpretation of Petronius’s Satyricon,
There is a story that when a certain lady of Ephesus, a woman of exemplary chastity, was widowed, she was not content with weeping for her husband in the usual manner, beating her breast at the funeral or further shutting herself away in inconsolable mourning; she went so far as to bury herself with her husband in an underground tomb. Here the model approaches myth, as the faithful wife treads the ground of the great heroines devoted to their husbands and condemned to grief beyond all consolation. This is the world of Evadne, Laodamia, Alcestis, Andromache, Dido. The grief of the widow of Ephesus, like that of certain heroines of the romantic novel, found satisfaction only in the longing for death, in the love-suicide that would unite the two partners. (p. 104, my emphasis)
Now we see how every part of the story fits. The spotlight is on the widow, not her deceased husband. It is her behaviour that the story is about. To all the world, or at least her neighbours, she appears to be the most devoted wife, another Dido who kills herself when her lover leaves, another Evadne who also commits suicide at the news of her husband’s death, another Laodamia who dies along with her husband when he is called back to Hades, and so on.
Petronius continues his story. The soldier brings food to the weeping widow who steadfastly refuses it. However, the servant of the woman yields and eventually persuades her mistress to eat. One thing led to another, and before long . . . .
‘Need I say more? The woman couldn’t refuse even this gratification of the flesh and the triumphant soldier talked her into both. They then slept together, not just the night they first performed the ceremony but the next night too, and then a third. The doors of the vault were of course closed, so if a friend or a stranger came to the tomb, he thought that the blameless widow had expired over her husband’s body.
 The reader now laughs at the hypocrisy, the falseness, of the woman found only in myth.
The reader now laughs at the hypocrisy, the falseness, of the woman found only in myth.
Meanwhile, the parents of one of the crucified victims saw that the guard was absent and took down their son to give him a proper burial. When the soldier returned from his liaison with the once-mourning widow and saw the body missing he feared he would be executed as punishment for deriliction of his duty. His new-found lover, however, came to his rescue by agreeing to allow him to replace the missing body with that of the husband she had not long before been wishing to die with. So with the widow’s urging he takes the husband’s corpse and places it up on the cross. And the widow and soldier, we presume, lived happily ever after.
The man for whom the world believed the woman was aching to die for is coldly dimissed and strung up in public disgrace so the woman could protect her new life of fickle indulgence.
If anyone can see an attack on Christianity in that little episode . . . . well, I do not see it. (And that’s before we even recall that the author of the Widow of Ephesus narrative (a part of the larger work Satyricon) is almost certain to have died before any of the Christian gospels were written.)
But if anyone wants to see a mockery of the mythical/legendary woman who resolves to die with her lost love one, then, just like Dido when she lost Aeneas and so forth, . . . yes, I can see that. Petronius even makes his theme unmistakably explicit.
Once again, we return to my post, Do Parallels Only Work in One Direction? Or bettter still,
.
Conte, Gian Biagio. 1997. The Hidden Author: An Interpretation of Petronius’s Satyricon. Berkeley: University of California Press.
Petronius. 2011. Petronius. the Satyricon. Revised Edition. Edited by Helen Morales. Translated by J. P. Sullivan. London: Penguin Classics.
Like this:
Like Loading...