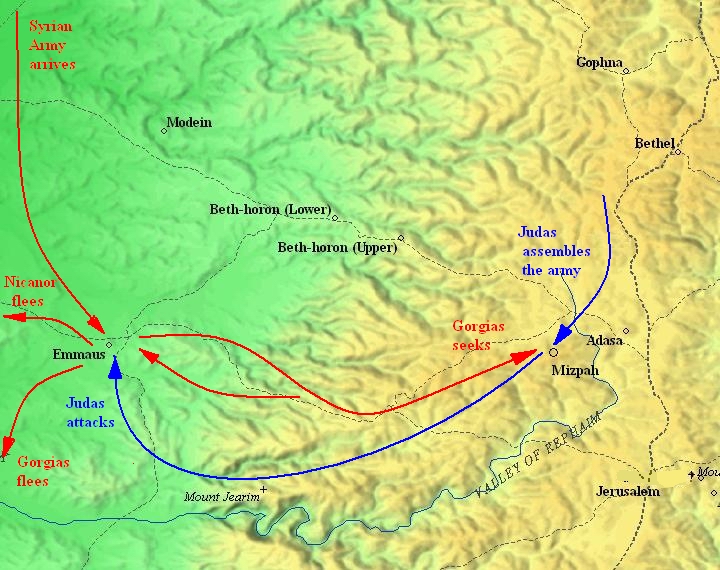
 In my previous post I quoted John Taylor where he referenced chapter 5 of Dionysus: Myth and Cult by Walter Friedrich Otto. That chapter is titled “The God Who Comes”. It is about this distinctive characteristic of the god Dionysus — that, unlike other gods, he comes to mankind visibly, that is, “in the flesh”. That post pointed to a strong theological or religious meaning that such a “historic presence” promised for ongoing and future intimate relations (even entering into the persons of devotees now) in the cults of both Dionysus and Jesus.
In my previous post I quoted John Taylor where he referenced chapter 5 of Dionysus: Myth and Cult by Walter Friedrich Otto. That chapter is titled “The God Who Comes”. It is about this distinctive characteristic of the god Dionysus — that, unlike other gods, he comes to mankind visibly, that is, “in the flesh”. That post pointed to a strong theological or religious meaning that such a “historic presence” promised for ongoing and future intimate relations (even entering into the persons of devotees now) in the cults of both Dionysus and Jesus.
For those who are too impatient to read that chapter online (it is available in its entirety on Google books) here are a few excerpts.
One could almost substitute “Jesus” and “Gospel of Mark’ or such for Dionysus and his narrative in the following discussion and one would continue to nod in assent with all that is said. Jesus is far from the violent figure towards humans that Dionysus is, but one reads commentaries on Mark speaking of the “violence” with which Jesus enters “history”, with his overpowering of demons and in other ways suddenly turning the world upside down. The same commentators speak of the urgency with which Jesus acts and demands responses from those he encounters. Continue reading “The God Who Comes”