Concluding an overview of Peter Kivisto’s discussion of “institutional openings to authoritarianism” in the USA. See Kivisto for the complete series. (Images, bolding, formatting, other sources are my additions.) The takeaway for me in Kivisto’s discussion is the pivotal role racism has played in enabling the presidency of Donald Trump. Little did I suspect that the Civil Rights Movement of the 1950s and 60s would lead what we see today in the political landscape. For another relevant perspective on Obama’s terms in office see the posts on Nancy Fraser’s From Progressive Neoliberalism to Trump – and Beyond. .
. . . . Republican Representative Joe Wilson upended congressional decorum by shouting that Obama was a liar while the President was giving a speech to a joint session of Congress. . . .
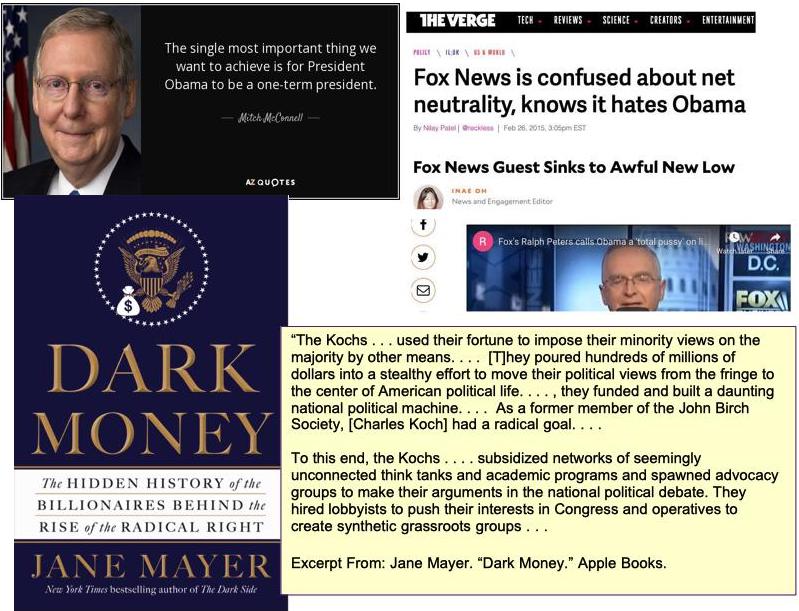
.. . . . The Republican leader in the Senate quickly promised that the one objective of Senate Republicans would be to insure that Obama would not be re-elected, and to that end rejected bipartisanship at every turn. The right-wing media savaged him relentlessly, the Southern Poverty Law Center reported disturbing increases in the size and activities of right-wing hate groups, and funds from right-wing plutocrats flowed freely to mobilize the grassroots. . . .
Obama had been exceedingly careful — too careful for many of his supporters’ tastes — in addressing issues about race. Moreover, he had to simultaneously confront two crises, the first being the blowback caused by the disastrous Bush/Cheney invasion of Iraq and the second being the global financial crisis that began in 2007. Much of his agenda reflected both the need to respond carefully to these inherited problems, but beyond that he pressed what was essentially a pragmatic center-left set of proposals. His one major ambitious plan called for building on the New Deal and Great Society programs in addressing the fact that the United States was the only wealthy liberal democracy in the world that did not treat health care as a universal entitlement. He sought to expand health care coverage, reduce costs, and implement best practices that would make for a more efficient and effective health delivery system. And in so doing, rather than pressing for a single-payer system akin to Canada’s or expanding Medicare to cover all Americans, he hoped for a plan that would elicit bipartisan support. To that end, the plan he proposed bore a family resemblance to one developed by a conservative think tank in the 1990s and a plan that Mitt Romney created in Massachusetts during his tenure as governor. Obstructionism would make bipartisanship impossible, and thus the Affordable Care Act was passed without a single Republican vote in either chamber of Congress.
In this context, the Tea Party came to represent the crystallization of citizen opposition to Obama. The intensity of their vehement hostility to Obama can be understood by the fact that as right-wing populists, their enemies were twofold:
- elites — governmental and academic, but not business
- — and the congeries of “Others,” including blacks, immigrants, Muslims, and freeloaders. . . .
. . . . He was the black usurper, his white mother in the end being irrelevant to this particular trope. He was the noncitizen, born in Kenya. He was the closet Muslim. At the same time, the Harvard Law graduate and part-time professor at the University of Chicago was a member of the elite liberal intelligentsia. Those who identified as strong Tea Party supporters, amounting to perhaps one-fifth of the electorate, were vocally unwilling to see Obama as a legitimate President.
Much discussion ensued about the precise character of the Tea Party. Was it a genuine grassroots movement or was it of the Astroturf variety, the product of the Koch brothers and other right-wing plutocrats? In The Tea Party and the Remaking of Republican Conservatism sociologists Theda Skocpol and Vanessa Williamson see it as both, observing that “one of the most important consequences of the widespread Tea Party agitations unleashed from the start of Obama’s presidency was the populist boost given to professionally run and opulently funded right-wing advocacy organizations devoted to pushing ultra-free-market policies.” These include FreedomWorks, the Club for Growth, the Tea Party Express, and Americans for Prosperity. The last of these is the creation of the Koch brothers, a nonprofit political advocacy organization. Its funders have spent millions pushing to privatize Social Security, voucherize Medicare and Medicaid, slash taxes, roll back environmental laws, and crush labor unions. For example, the organization shaped Governor Scott Walker’s assault on public sector unions in Wisconsin and has been a central player in shaping Rep. Paul Ryan’s agenda to roll back the welfare state. As oversight organizations promoting transparency have repeatedly pointed out, these operations are prime examples of the impact of dark money from wealthy right-wing donors who are able to keep their identities anonymous while spending freely to influence public policy.
 Continue reading “Obama, the Tea Party, and Assaults on American Democracy”
Continue reading “Obama, the Tea Party, and Assaults on American Democracy”