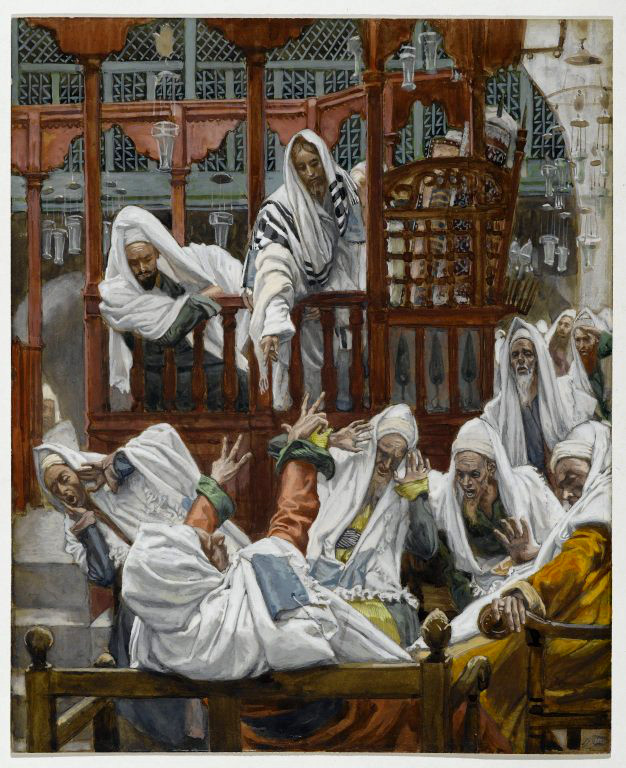
I have now returned to Australia from a regular overseas extended family visit, still somewhat sore from the accident I suffered over there, and in transit have been resisting the temptation to post easy “fillers” like more of the interesting differences encountered in Thailand or another response to an old McGrath post . . . hence the hiatus of the last few days. What has been on my mind, though, is some sort of extension to the previous post . . . Finally I settled on Mark 1:38 as the verse for the day. Jesus sneaked out of the house while it was still pre-dawn dark to find an isolated spot to pray. Eventually he was found by his disciples who complained that everyone had been looking for him. Jesus replied,
. . . . “Let us go somewhere else–to the nearby villages–so I can preach there also. That is why I have come.”
Such a mundane set of words. Nothing special…? But if we pause to think for a moment about that last sentence, “That is why I came”, — what was in the author’s (or, if you prefer, the mind of Jesus) when those words were expressed?
“Why I came”.
Am I reading too much (or too little) into the words when I wonder why he did not say, “That is why I have come back here” or even “that is why I came here”? Hadn’t Jesus grown up in Nazareth, Galilee? I read on one site that there is a twisty turny road from Nazareth to Capernaum (where Jesus was found praying) that extends around 40 miles:
But Jesus did not say “This is why I have come here (to Capernaum, or even to Galilee)” but “This is why I have come (ἐξῆλθον).” Luke changed what he read in Mark’s gospel to the more passive, “This is why I have been sent (ἀπεστάλην).” Mark’s Jesus did not say he was sent for a reason. Mark’s Jesus said he came forth for a certain reason.
And Mark’s Jesus does not appear to be telling his disciples that he came to Capernaum or to Galilee, but that he “came forth” . . . that is somehow more open-ended, more universalist, more existentialist — it is the reason Jesus came to . . . dare we say, to earth? Or at least to the lands where Judeans (or maybe only Galileans) were to be found?
Some readers may wonder what on earth I am getting at. The Gospel of Mark is widely accepted as the earliest of the written gospels and it is also widely understood to present the most “human-like” of the Jesus figures when we compare the Jesus in the other gospels.
But here in this simple sentence Jesus is depicted as saying that he came ….he came for a purpose. He was not “born” for a purpose. Or at least that’s not what he said.
Our minds have to go back to the beginning of the gospel. Where did Jesus come from?
John the Baptist was baptizing away and saying that someone greater than he was going to appear on the scene, then we are told that Jesus came to be baptized.
Now here it gets a bit complex and no doubt many readers will think I am overstepping “the mark” (pun not intended). Our text says Jesus came “from Nazareth”. I don’t believe that was what “Mark” wrote at all. I am convinced that “from Nazareth” are a copyists addition to the text. If you can bear with me and wait for me to offer reasons later, then accept my proposal that our purportedly earliest written gospel bluntly said that Jesus came . . . to be baptized. He came from nowhere. Thus said (or sort of implied) the text.
He simply came to be baptized. The narrative tells us nothing about his background or even who this Jesus character was. We are so familiar with the story and with far more than the story as told in this gospel that it is easy for us not even to notice how little (or even exactly what) Mark actually says.
Then when we come to Jesus’ being found alone with his God in Mark 1:38 he reminds us that we have not yet been told who this Jesus character is or where he has come from. (A comment by Martin anticipated this post.) Everything we have read so far has “only” told us that everyone (person or demon) who encounters him is over-awed by his authority. Everyone falls over backwards or drops their families and livelihoods or travels many miles merely on coming in contact with or simply hearing about his power of authority.
“For this reason I came forth” is not a quotidian remark about why he decided one day to leave Nazareth and visit Capernaum. It is a pointer to Jesus having come from heaven.
But that pointer is not likely to be noticed if we have our heads filled with the Gospels of Matthew and Luke before we read the Gospel of Mark. Continue reading ““This Is Why I Have Come” (from where?)”














