I have devoted my two previous posts to the part of my hypothesis that concerns the Pauline letters:
- The earliest parts of the original collection of Pauline letters were written between CE 50 and 130 by Simon of Samaria and his successor, Menander.
- Simonians were secretive, so the collection was likely intended for their use only.
- But by the early 130s some proto-orthodox Christians came to know of it and, by making certain additions and modifications, attempted to co-opt it for proto-orthodoxy.
|
 But at this point I expect that those who have read Robert M. Price’s book The Amazing Colossal Apostle are wondering: What about Marcion and gnostics like Valentinus? Didn’t they or their followers contribute something to the Paulines? Or, at least, weren’t they the targets of some of the proto-orthodox interpolations in the letters? Price would answer “yes” to these last two questions. His hypothesis is that:
But at this point I expect that those who have read Robert M. Price’s book The Amazing Colossal Apostle are wondering: What about Marcion and gnostics like Valentinus? Didn’t they or their followers contribute something to the Paulines? Or, at least, weren’t they the targets of some of the proto-orthodox interpolations in the letters? Price would answer “yes” to these last two questions. His hypothesis is that:
The Pauline epistles began, most of them, as fragments by Simon (part of Romans), Marcion (the third through sixth chapter of Galatians and the basic draft of Ephesians), and Valentinian Gnostics (Colossians, parts of 1 Corinthians, at least). Some few began as Catholic documents, while nearly all were interpolated by Polycarp, the ecclesiastical redactor who domesticated John (as Bultmann saw it), Luke (as per John Knox), and 1 Peter, then composed Titus and 2 Timothy. (The Amazing Colossal Apostle, p. 534)
One immediately noticeable difference between our hypotheses is that I hold, as argued in the previous post, that the original letters to the Ephesians and Colossians were written by the Simonian Menander, not Marcion or a Valentinian. To me, the passages that Price sees as Marcionite or Valentinian in these letters can just as plausibly be identified as Simonian. The theological development present in them is nothing that could not have already occurred within Simon’s communities in the generation after him, and thus before either Marcion or Valentinus are thought to have been active. Forty years—say, from CE 60 to 100—seems like plenty enough time for that development. And if so, the proto-orthodox interpolations could have been inserted with Simonians in view.
The proto-orthodox reworking of the letter collection could have been a fait accompli by the time Marcion and Valentinus went to Rome in the late 130s.
To illustrate my point, let’s consider some specific instances.
Ephesians
Price, in his commentary on Ephesians, writes:
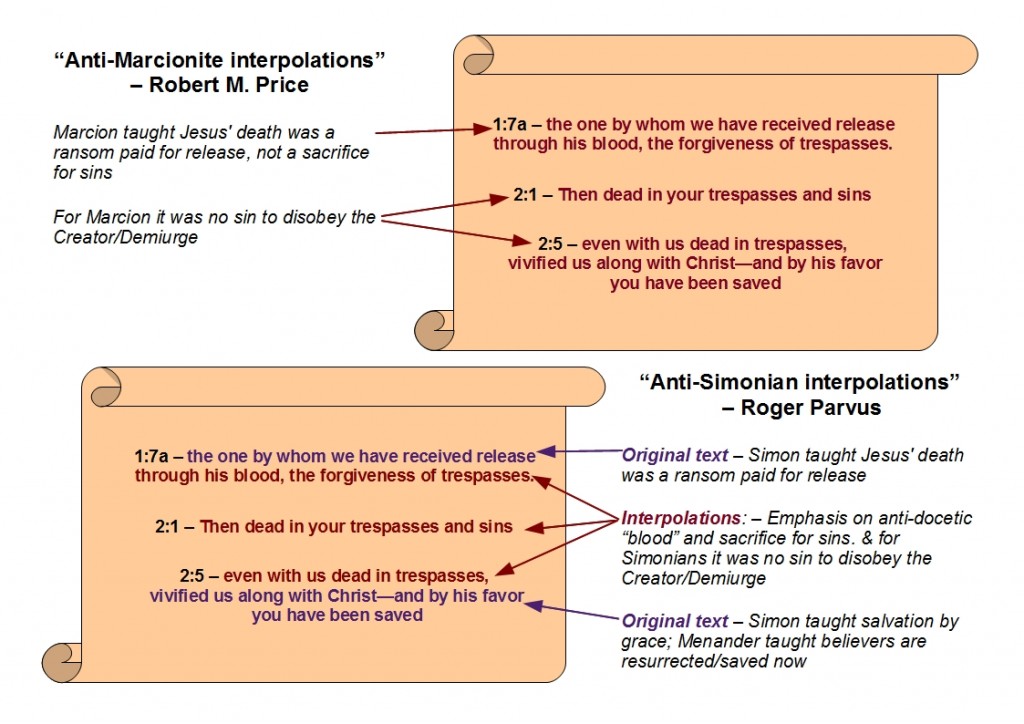
The first anti-Marcionite interpolation we can detect is in verse 1:7a, “the one by whom we have received release through his blood, the forgiveness of trespasses.” In Marcionite soteriology, the death of Jesus was a ransom, manumitting the enslaved creatures of the demiurge, not a sacrifice for sins. The same problem occurs in 2:5 where another insertion, “even with us dead in trespasses, vivified us along with Christ—and by his favor you have been saved,” attempts to correct Marcionite belief. Verse 2:1 likewise contains an anti-Marcionite interpolation, “then dead in your trespasses and sins.” No one was in trouble with the Father for having transgressed the commandments of the demiurge. (pp. 444-445 — Bolding added)
In regard to verse 2:5: I have already explained in my previous post how I would account for the realized eschatology expressed by “vivified us along with Christ.” This is not a doctrine the proto-orthodox interpolator would have added. It is rather a teaching of Menander that the proto-orthodox redactor allowed to remain in the text because it was rendered harmless by other offsetting insertions. Nor do I see the words “and by his favor you have been saved” as an interpolation. As already noted in my first post, Irenaeus clearly says that salvation by grace was a teaching of Simon of Samaria.
I do agree with Price that some tampering has occurred in the three verses in question. Specifically, I agree that the references to forgiveness of sin and trespasses have been added. These belong to proto-orthodox soteriology which put forward the death of the Son as an expiatory sacrifice or atonement for sin. But I’m not convinced these insertions were made to combat Marcionite belief. They could just as plausibly have been added to correct Simonian error. For ransom soteriology was not created by Marcion. In the extant proto-orthodox heresiological writings, the earliest figure to have a ransom soteriology attributed to him is Simon of Samaria.
 Simon taught that he was in some way inhabited by the Son who had previously appeared to suffer in Judaea. And as a new manifestation of that Son, he had come in search of his lost First Thought, Helen. He came in order to free her from the world-making angels who, by holding her captive, had prevented her from returning to her home above. The moment of her actual release from that captivity was apparently tied by Simon to his purchase of her from a brothel:
Simon taught that he was in some way inhabited by the Son who had previously appeared to suffer in Judaea. And as a new manifestation of that Son, he had come in search of his lost First Thought, Helen. He came in order to free her from the world-making angels who, by holding her captive, had prevented her from returning to her home above. The moment of her actual release from that captivity was apparently tied by Simon to his purchase of her from a brothel:
She [Helen] lived in a brothel in Tyre, a city of Phoenicia, where he [Simon] found her on his arrival… And after he had purchased her freedom, he took her about with him… For by purchasing the freedom of Helen, he thus offered salvation to men by knowledge peculiar to himself (Hippolytus, Refutation of All Heresies 6, 19).
Thus it appears that, because the salvation of Simon’s followers from this world and its makers was modeled on the salvation of Helen, theirs too was sometimes referred to as a purchase, ransom or redemption:
The dissolution of the world, they [Simonians] say, is for the ransoming of their own people (Hippolytus, Refutation of All Heresies 6, 19; my bolding)
Notice that the “ransoming” here is not a payment that will be made when the world is dissolved. It is not a payment made to anyone. It is simply release from this world. And from its makers, as comes through in the parallel passage of the Against Heresies:
Therefore he [Simon] announced that the world would be dissolved and that those who were his would be freed from the rule of those who made the world. (1, 23, 3)
The sense, then, of “ransom” appears to be release from those who keep one from returning home. That being the case, I would retain “the one by whom we have received release” in Eph. 1:7a as authentic, but reject the remaining words of the verse (“through his blood, the forgiveness of trespasses”) as an interpolation. The purpose of the interpolation was to make to make the “release” look sacrificial and expiatory much along the lines of so many passages in the proto-orthodox Letter to the Hebrews.
The use of the word “blood” in the interpolation had an additional proto-orthodox benefit—an anti-docetic one. A real sacrifice requires real blood, not the mere appearance of it. So connecting the “release” with blood also counters Simon’s teaching that the Son of God, at his first entry into the world, had merely appeared to be a man and merely appeared to suffer. But note again how there is no need to see Marcion as the docetic opponent targeted by 1:7a. He was not the first Christian docetist. The proto-orthodox heresy-hunters give that distinction to Simon of Samaria. Continue reading “A Simonian Origin for Christianity, Part 4: Excursus on Marcion, Valentinians, and the Pauline Letters”
Like this:
Like Loading...






 But at this point I expect that those who have read Robert M. Price’s book
But at this point I expect that those who have read Robert M. Price’s book 
