The two earlier posts on The Lord’s Prayer:
Let this be my third and final post on the Lord’s Prayer. I return to the article by Michael Goulder with which I began these posts.
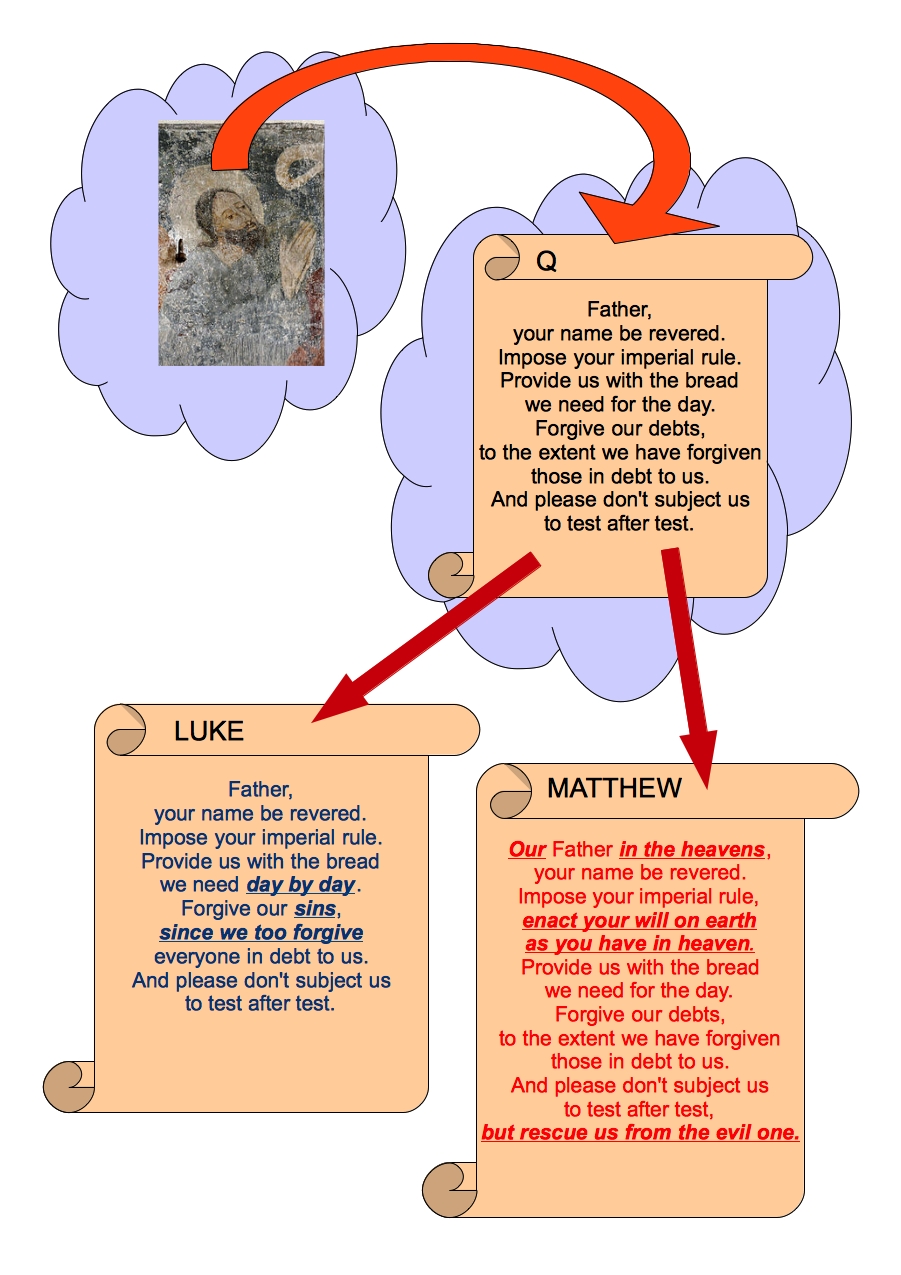
Our Father
I suppose by now it seems the most natural thing in the world to start the prayer with this address but it need not have been so. I suppose it could have begun, “Dear God”, “Great Lord”, “Creator of Heaven and Earth”, “Oh Ineffable One”, etc. But we have “Our Father”.
An explanation can be found in the writings that pre-dated the gospels. We learn there that addressing God as Father appears to have been widespread in Paul’s day:
Because you are his sons, God sent the Spirit of his Son into our hearts, the Spirit who calls out, “Abba, Father.” (Galatians 4:6)
The Spirit you received does not make you slaves, so that you live in fear again; rather, the Spirit you received brought about your adoption to sonship. And by him we cry, “Abba, Father.”(Romans 8:15)
The Gospel of Mark, the first gospel to be written (according to most studies today), carries over this custom when we find there Jesus himself praying, Abba, Father:
Going a little farther, he fell to the ground and prayed that if possible the hour might pass from him. “Abba, Father . . . “ (Mark 14:36)

Abba is the Aramaic for father, as we know. The word fell out of use, however, over time, so we see both the Gospels of Matthew and Luke dropping it and relying solely on the Greek word for father. So in Matthew’s and Luke’s copying of Mark’s scene above they drop Abba:
Going a little farther, he fell with his face to the ground and prayed, “My Father . . . “
He went away a second time and prayed, “My Father . . . “ (Matthew 26:39, 42)
Luke is even more truncated and omits the possessive pronoun:
He withdrew about a stone’s throw beyond them, knelt down and prayed, “Father, . . . “ (Luke 22:41 f)
So it is no great surprise to see Matthew’s Lord’s Prayer beginning with Our Father and Luke’s with Father.
Our Father in Heaven
Once again we begin with the earliest of the gospels, that of Mark, and a major source for both the gospels of Matthew and Luke. There we find only one time in which Jesus explicitly taught his disciples how to pray. It comes just after the disciples express amazement that Jesus’ curse on the fig tree really worked:
“Have faith in God,” Jesus answered. “Truly I tell you, if anyone says to this mountain, ‘Go, throw yourself into the sea,’ and does not doubt in their heart but believes that what they say will happen, it will be done for them. Therefore I tell you, whatever you ask for in prayer, believe that you have received it, and it will be yours. And when you stand praying, if you hold anything against anyone, forgive them, so that your Father in heaven may forgive you your sins.” (Mark 11:22-25)
That lesson on prayer in Mark (the only lesson on prayer in Matthew’s and Luke’s source) “coincidentally” introduces a major thought in the later Lord’s Prayer, the need to forgive sins of others so God will forgive us. It’s the main point of Jesus’ lesson on prayer in the Gospel of Mark and it is stressed in the Gospel of Matthew by added commentary at the end of the prayer as we shall see.
The point here, though, is that it is surely evident that the above Marcan passage was in the mind of the author of Matthew’s gospel, and there in Matthew’s source we find the same phrase, Father in heaven, as is used to introduce Matthew’s Prayer.
As we have seen in the previous post that Luke had already identified the Father he was talking about as being in heaven only 22 verses earlier so, in accord with his tendency to avoid repetition, he omits “in heaven” in his own version of the Prayer.
Forgive us our debts, as we also have forgiven our debtors
Continue reading “How Matthew Invented the Lord’s Prayer (A Goulder View)”